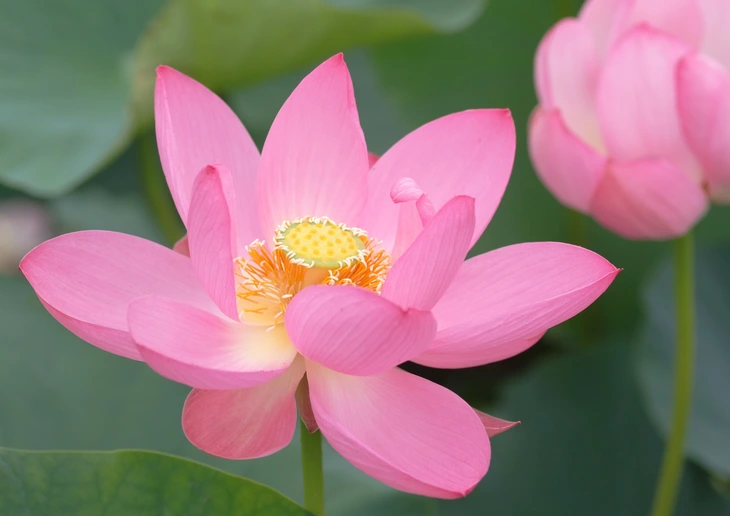

Japan's thousand-year-old lotus flower - Photo: GaijinPot Travel
Located about 60 km northwest of Tokyo is the Ancient Lotus Park. This place preserves and displays an ancient lotus species that was discovered by chance in 1971, when local authorities were digging the foundations for a waste treatment plant.
The strong vitality of ancient lotus flowers
Fossilized lotus seeds buried deep under the mud suddenly sprouted after centuries of dormancy when exposed to favorable environmental conditions, such as rainwater and sunlight.
After verifying the age, experts assessed this as a rare lotus variety, with special biological and archaeological significance.
According to Japan Travel , this lotus variety is called "Gyōda Hasu", which means ancient Gyōda lotus.
Since 2001, the local government has developed this place into an ecological park with about 120,000 lotus plants, belonging to 42 different varieties.
Among them, the ancient lotus variety occupies a special position with a graceful flower shape, fewer petals than modern varieties, and is said to have a shape close to the lotus's ancestors.
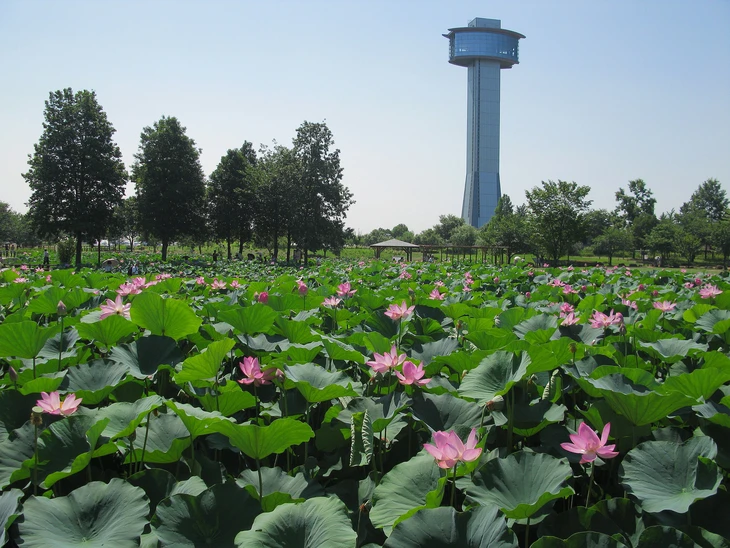

A corner of the Ancient Lotus Park in Japan - Photo: WIKIMEDIA
The flowering season usually starts from mid-June and lasts until early August. The best time to see the flowers is early in the morning, when the petals have not yet closed under the sunlight.
According to GaijinPot Travel , the morning from 7am to 9am is the busiest time.
In addition to the lotus pond, the park also has an Ancient Lotus Museum and a 50m high observation deck, where visitors can look out over the entire artistic rice fields and the vast lotus pond, part of the ecological space that has become a summer symbol of Gyōda.
Plants with the ability to repair DNA
The phenomenon of lotus blooming from ancient seeds has attracted special attention from the international scientific community. According to a research team from the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), lotus is a plant species with the ability to repair DNA particularly effectively.
“The lotus is the only plant known to have such a powerful self-repairing gene,” said biologist Jane Shen-Miller, who revived a 1,300-year-old lotus seed in China. “That’s why it can sleep for thousands of years and then come back to life when the conditions are right.”
In addition to its archaeological value, ancient lotus varieties such as Gyōda Hasu also open up many directions for applied research.
According to scientists, the resilience and resistance to biological stress of lotus can be exploited to improve the durability and resistance of modern crops such as rice, corn or soybean in the context of climate change.
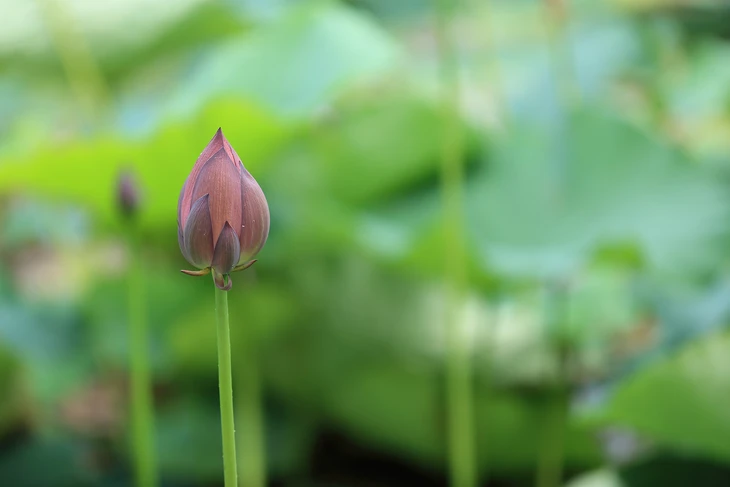

A Gyōda Hasu lotus bud - Photo: WIKIMEDIA
The story of the ancient Gyōda lotus seeds also recalls another famous seed recovery project carried out by Dr. Ichiro Oga in the 1950s, when he successfully germinated lotus seeds that were 1,000 to 1,300 years old at an archaeological site in China.
This lotus was later named “Oga Lotus” and is considered a symbol of enduring vitality that transcends time. According to the World Tribune , it was Oga’s discovery that inspired researchers in Japan to continue to recover and propagate the ancient lotus seeds found in Gyōda.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/hoa-sen-no-tu-hat-giong-1-400-nam-tuoi-20250707205720666.htm






























































































Comment (0)