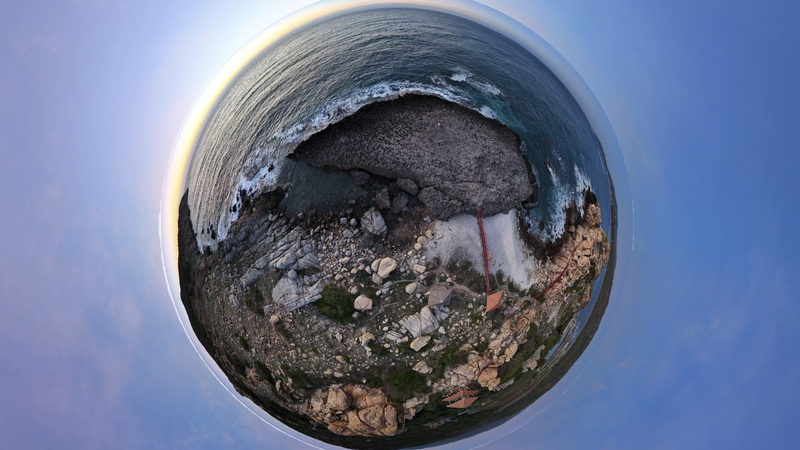
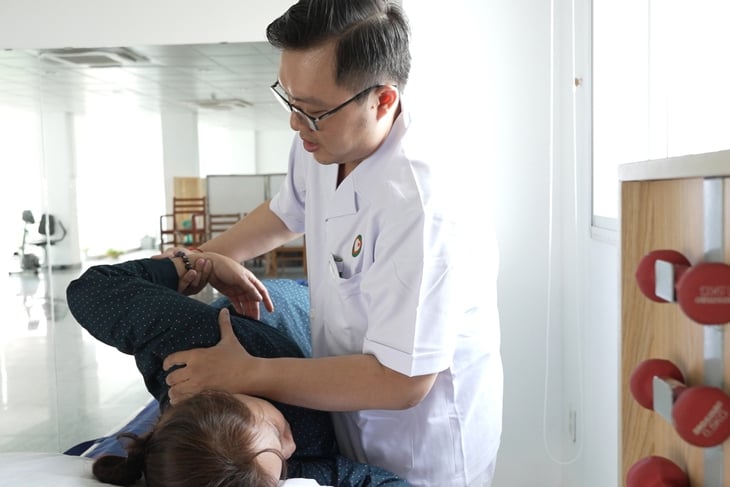
A recurrent stroke means a person's brain is deprived of oxygen at least twice, thus increasing brain damage - Illustration: thenewgait.com
Each stroke has the potential to cause brain damage, and multiple strokes can cause more severe damage and disability.
What is recurrent stroke?
A recurrent stroke is when a person has another stroke after having their first stroke.
A stroke deprives the brain of oxygen and causes significant damage to a patient's long-term neurological function. Recurrent strokes cause further brain damage, increasing the risk of disability and death.
According to studies, mortality rates are higher after a recurrent stroke. Specifically, survivors of a first ischemic stroke have a 1-year mortality rate of 17% and a 10-year mortality rate of 56%. These rates increase to 25% and 70%, respectively, if they have a recurrent ischemic stroke.
For recurrent hemorrhagic stroke, the 1- and 10-year mortality rates were 31% and 75%, respectively.
Stroke symptoms can vary and a person may have different symptoms when having a stroke again. Therefore, people who have had a stroke should quickly seek medical attention if they have unusual signs.
Causes of recurrent stroke
There are two types of strokes that can occur:
Ischemic stroke: caused by a blockage in a blood vessel that deprives the brain of blood and oxygen. Factors that cause this condition include: diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and obesity.
Hemorrhagic stroke: occurs when there is injury to a blood vessel or an aneurysm that ruptures, the main cause is often high blood pressure.
Symptoms of a recurrent stroke can be the same or very different from those of a person's first stroke.
Doctors diagnose recurrent stroke based on newly appearing neurological symptoms combined with new imaging evidence of damage (CT scan, MRI, angiography, etc.).
The prognosis is worse after a second stroke. The mortality rate is 2-3 times higher than that of a first stroke, the disability is more severe, lasts longer, and recovery is less likely. Therefore, you should go to the emergency room immediately if you have symptoms of a stroke.
Treatment of recurrent stroke
Treatment for a recurrent stroke is similar to treatment for a first stroke. However, treatment varies depending on the type of stroke (hemorrhagic or ischemic) the patient has.
After a stroke, patients need physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy to regain function.
After a stroke, patients need physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy to regain function.
Preventing recurrent stroke
Stroke prevention strategies need to be comprehensive, consistent, and individualized. Risk factors need to be controlled:
● High blood pressure is the leading risk factor, blood pressure should be maintained < 140/90 mmHg (or lower if indicated).
● Diabetes: good blood sugar control with HbA1C < 7.
● Atrial fibrillation and heart disease: consider anticoagulation when indicated.
● Lipid disorders: reduce LDL-C < 70 mg/dl.
● Stop smoking, maintain BMI < 25.
Recurrent strokes cause further brain damage, increasing the risk of death and long-term disability. Therefore, people who have had a stroke need to talk to their doctor to choose the appropriate treatment method to reduce the risk of recurrence: change your lifestyle, take the right medication, take it regularly, and follow up with regular check-ups as scheduled.
Dr. Pham Tran Xuan Hong is currently the head of the Department of Cardiology 5 - Cardiovascular Rehabilitation, Tam Duc Heart Hospital. She is an expert in the fields of: cardiovascular rehabilitation, valvular heart disease, heart failure, coronary artery, echocardiography, and vascular ultrasound.
Back to topic
MD.CKII PHAM TRAN XUAN HONG
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/dot-quy-tai-phat-rat-nguy-hiem-phong-ngua-ra-sao-20250704211753088.htm

































































































Comment (0)