Long-term exposure to air pollution increases the risk of respiratory diseases such as asthma, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and even lung cancer. In addition to wearing masks and installing air filters, adding some natural nutrients can also help support respiratory function, reduce inflammation, fight oxidation, and protect lung cells, according to the health website Verywell Health (USA).
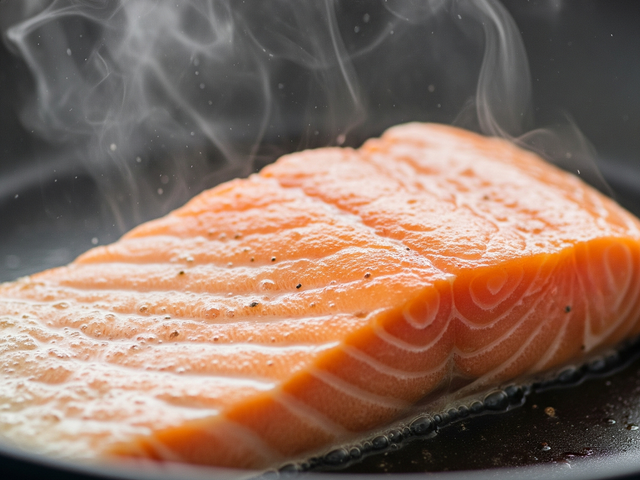

Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce systemic inflammation and are great for the lungs.
PHOTO: AI
Nutrients scientifically proven to help improve lung health, especially for people living in highly polluted environments, include:
Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid antioxidant found in onions, apples, and green tea. It is known for its powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In the presence of air pollutants, quercetin acts as a protector of lung cells from damage caused by free radicals produced by toxic gases and fine dust.
A study published in the Journal of Inflammation found that quercetin has the ability to inhibit inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6. These cytokines are key players in respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, are known for their ability to fight systemic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is one of the main causes of lung damage caused by air pollution.
Omega-3s interfere with the inflammatory response chain, reducing the activity of inflammatory mediators such as leukotrienes and prostaglandins. A study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine found that omega-3 supplementation reduced the risk of lung dysfunction in older adults living in areas with high air pollution.
N-Acetylcysteine
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) is a derivative of the amino acid cysteine, which has the properties of thinning phlegm, reducing bronchial congestion and increasing the synthesis of glutathione, one of the most important endogenous antioxidants in the body.
Research published in the Chest Journal found that NAC reduced sputum viscosity and protected against oxidative stress in lung tissue, thereby improving respiratory function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, according to Verywell Health .
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/can-bo-sung-chat-gi-de-phoi-khoe-18525070918343752.htm



![[Photo] Brilliant red of the exhibition 95 years of the Party Flag lighting the way before the opening](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/27/e19d957d17f649648ca14ce6cc4d8dd4)



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives CEO of Samsung Electronics](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/26/373f5db99f704e6eb1321c787485c3c2)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting of National Steering Committee on International Integration](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/26/9d34a506f9fb42ac90a48179fc89abb3)























![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends Meeting with generations of National Assembly deputies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/27/d869c6b3e4da42399e2cd0f4ca26050c)
































































Comment (0)