A few weeks ago, the US stock market saw a sell-off that wiped more than $1 trillion off the value of tech companies. The cause was not a financial crisis or a weak earnings report, but an announcement by DeepSeek, a Chinese startup, when it launched its artificial intelligence (AI) model R1.
What's worth mentioning isn't that R1 is as powerful as OpenAI's GPT-4, but that the model's strategy is completely free.
The decision is not an act of charity but a carefully calculated economic attack, the opening salvo in a national strategy to fundamentally change the way the world does business and makes money from AI. China doesn’t just want to compete, it wants to change the rules of the game by turning AI from a luxury to a common utility.
When "cheap" becomes the ultimate weapon
While giants like OpenAI, Google or Anthropic spend hundreds of millions of dollars, even billions of dollars, to build exclusive models and then resell access at high prices, China chooses the path of market dumping - a classic strategy in modern business textbooks.
The first crutch is cost. DeepSeek’s R1 model was developed on a budget of less than $6 million—a fraction of what it cost to build GPT-4.
China has achieved this by leveraging the power of older chips like the Nvidia H800, which are not subject to the US export ban. Instead of chasing expensive hardware, they have chosen a smarter way: optimizing costs to create a sustainable competitive advantage.
In addition, the “freemium” strategy that Chinese companies are adopting—offering a free but powerful model—shows that they are recreating the formula that helped Google and Facebook dominate the Internet: attract users, expand the developer community, and then figure out how to make money later.
Once Chinese AI becomes the standard among developers and businesses globally, it will only be a matter of time before it can be monetized. They can launch premium commercial versions, sell technical support, and even monetize data, all on a platform that was initially given away for free.
The most dangerous thing is the invisible but very real pressure this strategy puts on American companies. When the market is flooded with free AI models with near-premium product quality, who will want to pay millions of dollars for licenses?
This forces Western companies to cut prices, thin profit margins or prove that their products are superior – an increasingly difficult requirement as the quality gap narrows.
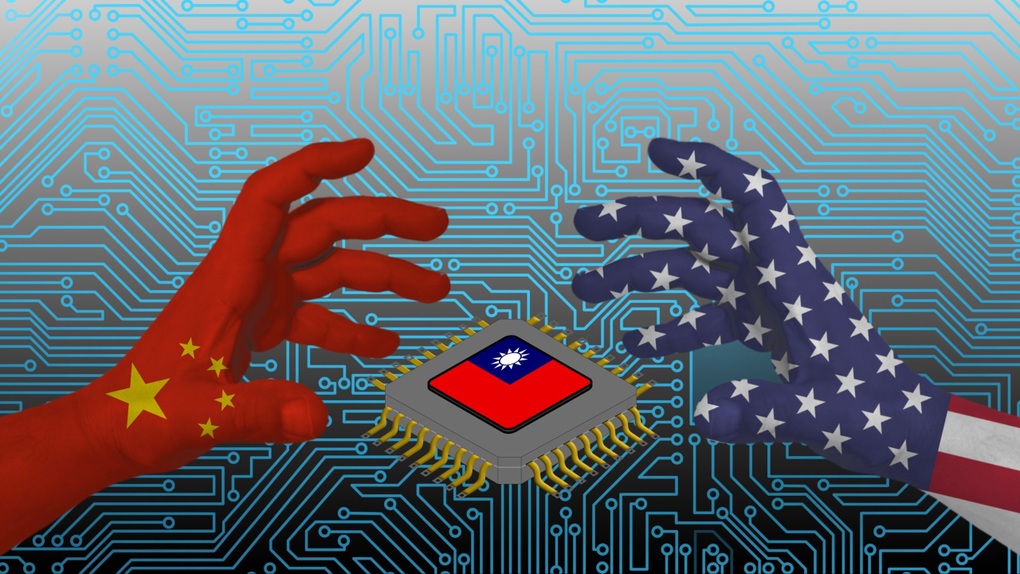
DeepSeek's AI breakthrough sends US tech stocks plummeting (Photo: Techwireasia).
National Infrastructure Machine: The Foundation for the Long Game
For the “free AI” strategy to succeed, companies need a robust and cheap infrastructure to operate on. And this is where the role of the Chinese state comes into play.
Beijing is rolling out a plan to build more than 250 dedicated AI data centers across the country, essentially a massive government subsidy program, according to a report from Strider Technologies.
By investing in computing infrastructure, the government significantly reduces operating costs for domestic AI companies. It also allows them to maintain a free-to-use business model for a long time, stifling competitors.
This ambition extends even further into space, with plans to deploy thousands of satellites that will act as data centers in orbit. Economically, this will create a unique advantage: the ability to collect and process data almost instantly, opening up entirely new business models in areas such as logistics, smart agriculture and finance. This is a long-term investment to control the entire value chain of the data economy.
Trade barriers and risks that cannot be ignored
While China's strategy is well-thought-out, it faces significant economic and trade barriers.
The biggest risk is not technology, but trust. Are international businesses, especially those in the West, willing to entrust their most sensitive business data to an AI model trained and operated in China’s censored internet environment?
Content censorship and data security issues are huge trade barriers that could limit China's AI's ability to penetrate global markets.
Moreover, the market is always reacting. Under pressure from China's open models, American companies are not sitting still. Meta has pioneered the open-source Llama model, and Elon Musk has also open-sourced Grok. The battle is gradually shifting from "closed vs. open" to a competition to see whose open ecosystem is better, safer, and more trustworthy.
The Economic Future of AI: The Race for Business Models
The rise of Chinese AI demonstrates an important truth: the AI race of the future will not just be a race for the strongest technology, but a race for the most sustainable business model.
Silicon Valley is used to selling tech products at high profit margins. But China is betting that AI will go the way of cloud computing or open source software—where prices keep falling and the game goes to those with the biggest scale and lowest cost.
This economic bet is forcing the world to rethink. Will the future of AI be a premium service, or a basic utility that everyone can access? The answer will shape not only the technology industry, but the entire global economy for decades to come. And right now, China is betting the most aggressively on a free future.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/kinh-doanh/ai-mien-phi-trung-quoc-thach-thuc-thung-lung-silicon-20250710165519671.htm







![[Photo] People eagerly lined up to receive special publications of Nhan Dan Newspaper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/30/53437c4c70834dacab351b96e943ec5c)



























































































Comment (0)