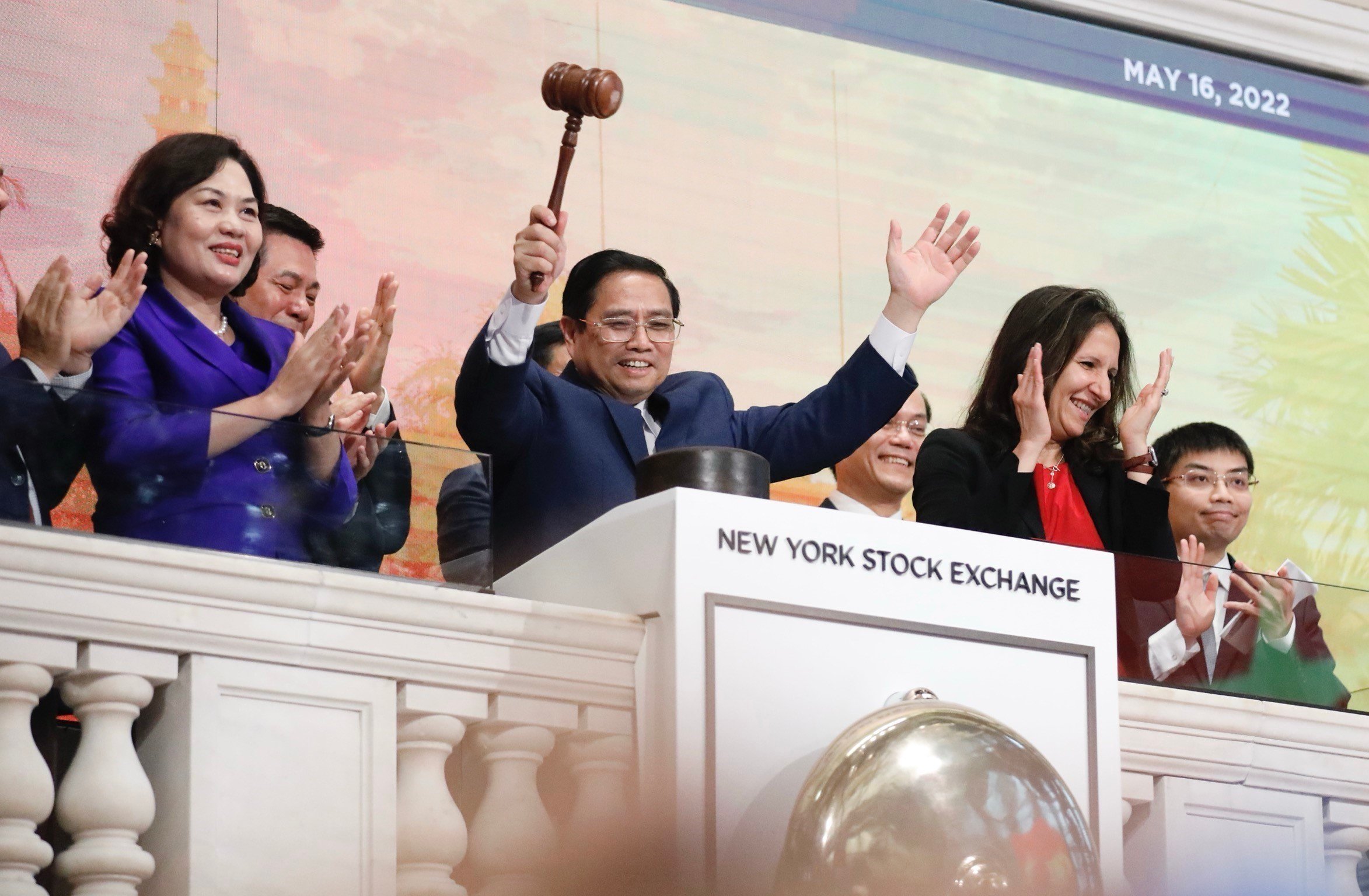
Politburo member and Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh bangs the gavel to end the trading session at the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) on May 16, 2022_Photo: VNA
Overview of the financial center
According to Investopedia, a Financial Hub is a city or area where many financial service institutions are headquartered (1). A financial center is a stock exchange and other financial service companies. A financial center develops in an area supported by government policy regulations. According to Businessdictionary, a financial center is a city or area with the following characteristics: 1- Concentration of many financial institutions; 2- Providing advanced commercial and communications infrastructure; 3- A large amount of domestic and international commercial transactions are conducted. Thus, in general, the approaches are consistent in describing a financial center as a geographical area (at the city level or equivalent) in which the financial sector is highly developed, reflected in the concentration of many large banks and financial institutions, developed infrastructure and other factors serving the smooth and rapid conduct of financial transactions.
Financial centers help increase efficiency and allocate financial resources. Currently, the banking system and financial markets are developing strongly. However, if financial tasks are concentrated in a large-scale center, it will create better connections between domestic and international capital sources, improve the ability to mobilize capital for important projects, and contribute to accelerating economic development.
In addition, the financial center attracts international financial institutions and high-quality foreign direct investment (FDI) capital flows. A transparent investment environment, clear legal framework and modern infrastructure can completely become an ideal destination for financial corporations and international investors. Thereby, bringing abundant capital and promoting the transfer of advanced financial technology and knowledge to the economy.
In the context of increasingly fierce regional competition, having an international financial center helps affirm the country's role and position in the global economic network, thereby expanding opportunities for international cooperation and deeper participation in international financial organizations.
The financial center is also a place to connect regional and international finance. The financial center will link with major international financial centers in the region to take advantage of capital management and international financial flows. At the same time, promote financial and trade cooperation mechanisms with other countries, creating conditions for cross-border capital flows into the country.
Building a regional and international financial center will help diversify capital flows, open up opportunities to become a high-income country, and promote sustainable development. However, this is a difficult, complex, and new issue.
International experience in building and developing financial centers
New York Financial Center (USA)
New York began as a Dutch trading post in 1624. Its natural harbor location facilitated the growth of trade. In 1792, 24 merchants signed the Buttonwood Agreement on Wall Street, pledging fixed commissions on trading, laying the foundation for the NYSE - the world's largest stock exchange. Since then, New York has been one of the world's largest financial centers, influencing global finance.
The city's regulatory system has played a vital role in maintaining its leading position for centuries. With a history of hundreds of years of formation and development, New York's regulatory system was developed very early. This created a solid and extensive foundation for managers when experiencing many global economic and financial crises. The regulatory framework of the New York Financial Center stands out for its complexity, comprehensiveness and flexibility. The regulatory system governing the operations of the New York Financial Center includes many different laws and detailed regulations on specific fields, such as securities, banking, insurance and other specialized financial fields. The laws and regulations are always updated to suit each specific period. In addition, investor protection and market transparency are top priorities as companies listed in New York must comply with strict regulations on financial information disclosure, ensuring transparency and helping investors make informed decisions.
Some typical laws and regulations related to the operations of the New York Financial Center are the Securities Acts of 1933 and 1934, the Dodd-Frank Act, the Model Business Corporation Act, the Mergers and Acquisitions Regulations, etc. In particular, the Securities Acts of 1933 and 1934 require companies to comply with strict regulations on the disclosure of periodic financial information and important information, prohibiting insider trading, that is, using unpublished information to buy and sell securities for personal gain. This helps ensure market transparency and protects small investors from the risk of information exploitation. The Dodd-Frank Act was enacted after the global financial crisis in 2008, requiring large financial institutions to conduct regular stress tests to assess the organization's resilience to market shocks. This helps prevent financial crises like the one in 2008. The Act provides for consumer protection in the financial sector, such as clear regulation of complex financial products and enhanced consumer rights when making complaints. The Model Companies Act provides a flexible framework for companies, allowing them to design their own governance structures and business operations, but still within certain regulations. New York has a clear and transparent process for mergers and acquisitions (M&A), protecting the rights of shareholders of companies involved in the transaction, and antitrust regulations ensure that M&A transactions do not reduce competition in the market.
Financial Center London (UK)
London was one of the first financial centers in the world and once formed the London-New York financial axis with the ability to control the entire world's finance. The Industrial Revolution in England marked the formation of the London Financial Center when industries developed strongly, creating a large demand for capital and finance. London quickly became the financial center serving this need. By the end of the 19th century, the financial group in the City of London increasingly expanded to provide financial services to the global economy. International trade grew rapidly while the banking system developed worldwide. The London money market benefited by withdrawing money from all over the world to finance international trade, with the Bill of London becoming a popular tool of global trade.
The regulatory framework of the London Financial Center has a number of outstanding features, such as stability, flexibility, investor protection, and high internationality. The Common Law system is the foundation of the English legal system. This system is formed from court decisions over many centuries, creating high flexibility and adaptability for business activities, especially in the financial sector. The Companies Act regulates the establishment, management and dissolution of companies in the UK, ensuring transparency in company operations and protecting the rights of shareholders. In addition, this law is regularly amended and updated to suit the development of the market and technology. Investor protection is a top priority in London with a number of typical laws and regulations such as the Financial Services and Market Act to ensure the stability and fairness of the UK financial market, prevent fraud and insurance regulations in the UK to protect consumer rights, ensure insurance companies operate fairly and transparently.
Financial Center Singapore
Unlike the two long-standing financial centers in New York and London, Singapore really began the process of becoming a financial center in Asia after gaining independence in 1965. In 1968, Singapore established the Asian Dollar Market, allowing foreign banks to operate there. This decision laid the foundation for Singapore's development as a regional financial center. Singapore has continuously developed new financial products and services to meet the needs of domestic and foreign investors. Many multinational companies choose Singapore as their regional headquarters or financial center thanks to its political and social stability, modern infrastructure, and skilled workforce, contributing to strengthening Singapore's position on the world financial map. At the beginning of the 21st century, Singapore recorded impressive growth in the financial services industry. According to the Monetary Authority of Singapore (2002), assets under management increased by 11% between 2001 and 2002. Singapore drives much of the merger and acquisition activity in the region. According to the Global Financial Index (2023), Singapore's financial centre ranks 4th globally, behind New York, London and Hong Kong (China).
The regulatory framework of the Singapore Financial Centre is similar to that of the London Financial Centre with Singapore adopting Common Law. The common features of the regulatory framework of the Singapore Financial Centre are transparency, stability, consistency, continuous updating and investor protection with typical laws, such as the Company Law, which regulates the procedures for establishing, registering and dissolving companies, providing corporate governance principles, requiring disclosure, and periodic financial reporting according to international accounting standards (IFRS); The Financial Services and Markets Act (FSMA) sets out the general legal framework for supervising and regulating activities in the financial markets, including banking, securities, insurance and financial derivatives, regulating the licensing of financial institutions, capital requirements, operating standards, providing regulations to protect investors' rights, enhance transparency and fairness in the market, regulating violations of the law in the financial sector, including fraud, market manipulation and money laundering; the Securities Law regulates the listing of securities, securities trading, issuance of bonds and financial derivatives, regulating the activities of securities companies, brokers and other intermediaries in the securities market, requiring listed companies to disclose information fully and promptly.
Stock exchange in Singapore_Source: Bloomberg
Towards a regional and international financial center - Some issues raised from the policy perspective
To build a regional and international financial center, establishing a solid, transparent and modern legal framework is a prerequisite. An effective financial center requires not only a perfect legal system, but also a favorable business environment, investor protection mechanisms and strong public-private cooperation. Below are some issues that can be drawn from the experience of developing regional and international financial centers.
First, perfect the legal system.
One of the most important factors in developing a financial center is to build and perfect the legal system in accordance with international practices and standards. This requires the rapid completion of legal regulations related to enterprises, securities, banking, and insurance. This is not only to improve compatibility with global standards, but also to ensure the ability to respond quickly to changes in the financial market. Many legal documents, such as the Law on Enterprises, Securities, Credit Institutions, Insurance, etc., need to be reviewed and adjusted to suit practical needs and technological advances. In addition, it is extremely urgent to issue new regulations to regulate emerging areas, such as financial technology (fintech), systemic risk management, and personal data protection. With the strong development of technology and digitalization trends, the lack of clear regulations can lead to great legal and financial risks. In particular, consistency between legal documents is an important factor in creating a stable legal environment, attracting domestic and foreign investors.
Second, create a favorable and transparent environment.
Another equally important factor is improving the business environment through streamlining administrative procedures and reducing legal compliance costs for businesses. The complexity and high costs of law enforcement often cause difficulties for investors, reducing the attractiveness of the domestic financial market. Simplifying procedures can create a favorable environment for investors, while improving their competitiveness in the international market. Furthermore, requiring financial institutions to disclose information fully and promptly is a necessary factor to ensure transparency in the market. Clarity in information helps build investor confidence, contributes to increasing market stability and attracting more capital from international investment funds.
Third, protect investors.
To ensure the sustainable development of the financial market, protecting the rights of investors is extremely important. The State needs to establish a strong enough legal mechanism to prevent fraud, abuse of power or personal gain in the process of financial activities. This includes strict handling of violations of the law by individuals and financial institutions. In addition, the establishment of an Investor Protection Fund can play an important role in protecting the rights of investors when disputes arise or when a financial institution becomes insolvent. Appropriate insurance tools also need to be deployed to ensure that investors are protected against unwanted financial risks.
Fourth, promote financial education and awareness raising.
Financial education plays an indispensable role in helping investors, especially those new to the market, to make informed decisions. The State and financial institutions should coordinate to organize training programs and seminars to improve investors' financial knowledge and skills. When investors have a deeper understanding of financial products, they will easily identify investment risks and opportunities, thereby better protecting themselves in a volatile market context. Raising awareness not only helps protect investors, but also creates a knowledgeable investment community, contributing to the stable and sustainable development of the financial market. Knowledgeable investors will minimize risky investment decisions, thereby minimizing the possibility of causing liquidity problems or systemic risks.
Fifth, encourage public-private partnership (PPP).
Public-private partnerships can bring many benefits to the development of financial infrastructure and support services related to financial centers. It is necessary to create conditions to encourage private sector enterprises to participate in the construction of important infrastructure works through appropriate forms of cooperation. This will not only help reduce the financial burden on the state budget, but also open up development opportunities for private sector enterprises and promote innovation in the financial industry. In addition, combining resources from both the public and private sectors will create a more comprehensive and sustainable financial ecosystem, meeting the growing development needs of the domestic financial market.
The construction of a financial center is a testament to the prestige and development of an economy. The practical operations of financial centers in London, New York, Singapore, and Hong Kong (China) have clearly affirmed that. The research on the construction of regional and international financial centers in Vietnam plays an important role and significance in promoting economic growth.
--------------------
(1) Will Kenton: “Financial Hub: What it Means, How it Works”, https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/financial-hub.asp
Source: https://tapchicongsan.org.vn/web/guest/the-gioi-van-de-su-kien/-/2018/1103002/xay-dung-trung-tam-tai-chinh-khu-vuc-va-quoc-te--kinh-nghiem-quoc-te-va-mot-so-van-de-dat-ra-tu-phuong-dien-chinh-sach.aspx




































































































Comment (0)