(NLDO) - Ancient humans, who lived on Earth 800,000 years before modern humans, evolved much faster than we once thought.
In the Olduvai Gorge in the Ngorongoro Conservation Area in Tanzania, scientists have found shocking evidence of a tool-making “factory” that predates our modern species, Homo sapiens, by 800,000 years.
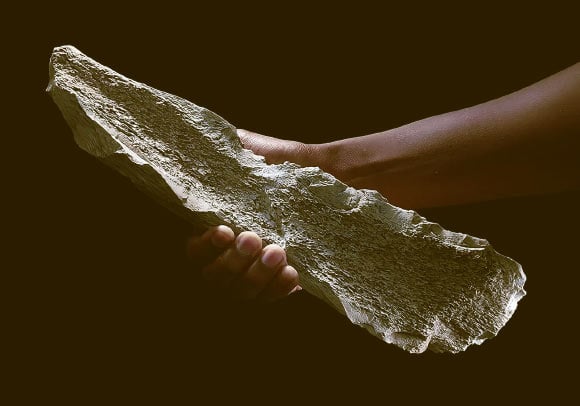

One of the bone tools created by a mysterious ancient human species in Tanzania - Photo: NATURE
According to Sci-News, a team of authors led by Dr. Ignacio de la Torre from the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) found 27 strange bones at a cluster of relics inside the famous mountain range in the above-mentioned reserve, a world heritage site recognized by UNESCO.
These are 27 bones taken from the front and hind legs of large mammals, mainly elephants and hippos, shaped into tools with certain standards.
This suggests that as early as 1.5 million years ago, a primitive type of factory was established at this site, operating not unlike modern human factories, albeit on a smaller and more rudimentary scale.
Before that, ancient humans had already used stone tools. But the switch to bone tools was another big step, one that paleoanthropologists once thought could only happen about 500,000 years ago.
The site in Tanzania pushes that milestone back by a million years.
“This technological expansion shows advances in their cognitive abilities and mental structures, who knew how to incorporate technical innovations by applying their knowledge of stonework to bone processing,” said Dr Torre.
Meanwhile, co-author Renata Peters from University College London (UK), said these bone tools showed that their creators carefully processed the bones, chiseling each piece to create useful shapes.
She described it as “a level of cognitive sophistication that we have not seen anywhere else” during the same period.
The earliest human stone tools date back to the Oldowan period, about 2.7–1.5 million years ago. Tools from that period were made simply by chiseling out a few pieces from a stone core with a stone hammer.
The bone tools described in the current study date from the time of ancient human ancestors entering the Acheulean period, which began about 1.7 million years ago.
Acheulean technology is best characterized by the use of more complex hand axes, carefully shaped by chipping, allowing tool production through more standardized means.
Still, the discovery that this technology was soon applied to bones suggests that scientists may have to rewrite human history, as it becomes clear that these ancestors were much closer to us in evolution than we once thought.
The study was recently published in the scientific journal Nature.
Source: https://nld.com.vn/phat-hien-nha-may-15-trieu-tuoi-viet-lai-lich-su-loai-nguoi-196250307095800075.htm




![[Photo] The first meeting of the Cooperation Committee between the National Assembly of Vietnam and the National People's Congress of China](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/31/f5ed4def2e8f48e1a69b31464d355e12)
![[Photo] Marching together in the hearts of the people](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/31/8b778f9202e54a60919734e6f1d938c3)

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Chairman of the National People's Congress of China Zhao Leji](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/31/5af9b8d4ba2143348afe1c7ce6b7fa04)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man welcomes and holds talks with Chairman of the National People's Congress of China Zhao Leji](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/31/9fa5b4d3f67d450682c03d35cabba711)






















































































Comment (0)