EGCG is a compound belonging to the catechin group, which is highly abundant in green tea leaves, with strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and tissue regeneration support properties. According to in vitro and in vivo studies, EGCG participates in many biological mechanisms such as regulating inflammatory responses, reducing oxidative stress, stimulating blood vessel formation and inhibiting the growth of harmful microorganisms on the skin.
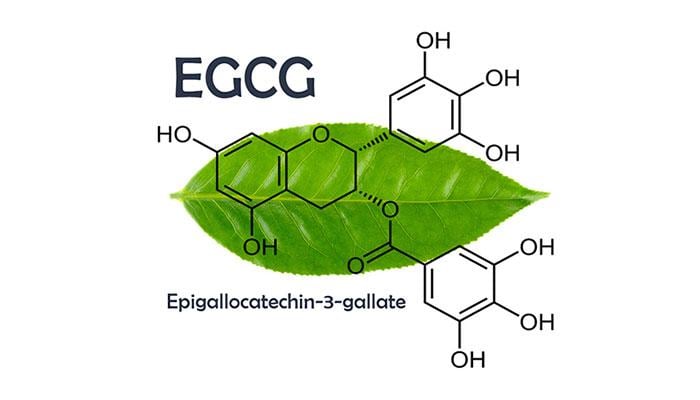
Molecular structure of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) found in green tea leaves.
Supports wound healing and skin care
According to a synthesis of studies on cells and animal models, EGCG can affect three main stages of the wound healing process: inflammation, proliferation and re-epithelialization. The mechanism of action of EGCG is believed to come from its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
EGCG has antioxidant properties that help reduce the concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby facilitating the activation of cell signaling pathways and promoting angiogenesis. As a result, EGCG contributes to reducing the risk of oxidative stress - a factor that can hinder tissue repair and lead to the formation of chronic wounds.
EGCG has also been shown to inhibit the activity of several common bacteria that cause wound infections, including Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli, and to prevent biofilm formation, one of the causes of slow wound healing.
Support treatment of cancer, nerves, diabetes
Not only in dermatology, EGCG has also received attention from many research groups in supporting the prevention and treatment of cancer, thanks to its ability to inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9. In a small clinical study, EGCG showed a high level of prostate cancer prevention in patients with prostatic hyperplasia when used at a dose of 600 mg/day.
EGCG is also considered to be effective in protecting nerve cells, fighting damage caused by amyloid beta (Aβ) - the main cause of Alzheimer's disease, and improving spatial cognitive learning ability in mice.
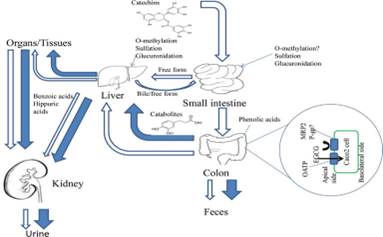
Diagram of metabolism and biological effects of EGCG in the body.
In addition, this active ingredient also has the effect of supporting blood sugar reduction, improving blood lipid indexes and promoting weight loss. The blood sugar reduction effect of EGCG has been proven through a clinical trial on patients with type 2 diabetes, using a dose of 300 mg/day for 8 weeks. In addition, the use of EGCG for 12 weeks also showed a significant reduction in LDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels in a group of obese women aged 16 to 60. These effects may be related to the mechanism of AMPK activation in the liver, skeletal muscle and white adipose tissue.
Opportunities from domestic raw materials
Vietnam is one of the leading countries in the tea industry. According to Agro.gov.vn, the tea growing area in Vietnam is currently estimated at about 125,000 - 130,000 hectares, mainly concentrated in the northern mountainous provinces such as Thai Nguyen, Phu Tho and some areas in the Central Highlands such as Lam Dong. The Department of Crop Production - Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (now the Department of Crop Production and Plant Protection - Ministry of Agriculture and Environment ), Vietnam's tea output in 2023 is estimated to reach nearly 200,000 tons of dry tea, with an export volume of more than 120,000 tons, mainly in the form of green tea, ranking 5th in the world.
In addition to the main product of tea buds, each year the Vietnamese tea industry discharges about 1 million tons of tea scraps and dried tea leaves. These by-products contain about 3 - 5% EGCG. It is estimated that thousands of tons of EGCG can be refined from these by-products to create a proactive source of raw materials for the domestic and export pharmaceutical, food and cosmetic industries.
Application of science and technology in tea production and processing
With great potential in domestic raw materials, tea plants - especially Thai Nguyen tea - are being identified by the Vietnam - Korea Institute of Science and Technology (VKIST) as a strategic research subject in the field of biotechnology. The goal is to maximize the value of the precious active ingredient EGCG, contributing to the creation of value-added products for health care and beauty, targeting both domestic and export markets.
According to Associate Professor, Dr. Phuong Thien Thuong - Deputy Director of VKIST, current cooperation projects are focusing on developing the technological process of extracting and purifying EGCG from Thai Nguyen tea materials, and at the same time researching the application of nanotechnology to improve the bioavailability of this active ingredient. By converting EGCG into nanoEGCG, the absorption capacity and biological efficiency of the active ingredient will be enhanced, opening up great prospects in the development of high-quality pharmaceutical, cosmetic and functional food products.
Currently, VKIST is also cooperating with Viet Bac L'Héritage Joint Stock Company and FiboLab Technology Investment Joint Stock Company with the goal of: "Cooperating in investment in refining and producing EGCG, nanoEGCG compounds and high-tech products from tea plants in Thai Nguyen province on an industrial scale." The agreement lays the foundation for the formation of a closed value chain from tea raw material areas to high-tech products, contributing to enhancing the value of Vietnamese tea brands in the international market.
Source: https://mst.gov.vn/epigallocatechin-gallat-hoat-chat-quy-tu-cay-che-viet-nam-voi-tiem-nang-ung-dung-trong-cham-soc-suc-khoe-va-lam-dep-197250716181334477.htm




















































![[Maritime News] More than 80% of global container shipping capacity is in the hands of MSC and major shipping alliances](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/16/6b4d586c984b4cbf8c5680352b9eaeb0)











































Comment (0)