Family pets can carry worms and bacteria that can infect people and cause diarrhea, fever, and itching; proactive prevention is needed.
MSc. Nguyen Dieu Thuy, medical specialist of VNVC Vaccination System, said that raising pets is a trend that many people love. Animals chosen as pets are very diverse, commonly dogs, cats, hamsters, and birds. Each species can contain many pathogens and transmit them to humans.
Parasitic infection
Many pet owners have the habit of playing with, sleeping with, and treating their pets as close friends. However, these actions pose a high risk of infection with animal parasites.
For example, cats have the parasite Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii), which causes toxoplasmosis. This parasite is common worldwide , and infected people do not show symptoms. However, toxoplasmosis can cause serious complications in people with compromised immune systems and pregnant women, such as eye and brain infections, birth defects, and miscarriages. Children born with the parasite may have brain and eye problems, seizures, developmental delays, or blood disorders.
Pet owners can also be infected with roundworms in cats and dogs, causing itchy rashes, hives, headaches, convulsions, prolonged fever, vestibular disorders, and insomnia. Worms can form tumors in organs such as the liver, heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, eyes, muscles, etc., or platelet dysfunction leading to bleeding and encephalitis.

Children can get worms from contact with dogs and cats. Source: Today Show
Hookworms can be transmitted to humans through skin contact, hugging and kissing dogs and cats, or walking barefoot on wet ground mixed with animal waste. Symptoms of hookworm infection include coughing, chest pain, wheezing... The disease can become severe, causing anemia, protein deficiency, emaciation, and heart failure.
Campylobacter diarrhea
Campylobacter bacteria are commonly found in poultry, cats and dogs. The main route of infection is through food, for example, eating undercooked meat, raw or contaminated milk, animal waste, and contaminated water.
According to the World Health Organization, Campylobacter is one of the four main causes of diarrhea, and is the most common cause of gastroenteritis. People infected with this bacteria usually have mild illness; young children, the elderly, and the immunocompromised can die. There is currently no approved vaccine in the world, only one vaccine candidate is in clinical trials.
Rabies
Rabies is currently among the most dangerous infectious diseases with a high mortality rate in humans in Vietnam. The disease is transmitted to humans through bites, scratches or contact with open wounds or licks from animals. According to statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), each year about 59,000 people die from rabies and more than 10 million people must be vaccinated against rabies. Vietnam records an average of 75 deaths from rabies each year. Every year, about 400,000 people bitten by dogs and cats must receive preventive treatment with rabies vaccines, at an estimated cost of more than 300 billion VND.
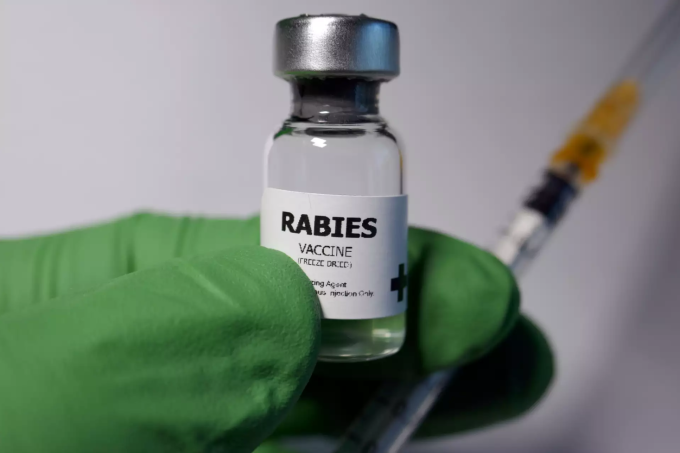
Rabies vaccination is a measure to prevent disease and reduce deaths. Source: Healthworld
How to prevent disease?
People should avoid eating raw or undercooked meat, wash kitchen utensils, fruits and vegetables thoroughly. If there are small children in the family, they should avoid playing in areas with cat waste, do not allow cats in the kitchen, and do not adopt stray cats or dogs.
Every week, families need to clean up the area where pets lie. Dog, cat, and pet feces should be buried or put in a sealed bag and thrown in the trash. Families should regularly deworm and vaccinate dogs and cats against rabies, and wash their hands after playing with pets.
As for rabies, there is a vaccine, usually given after being bitten or scratched by an animal or as a preventive injection for veterinary staff who regularly come into contact with animals.
Currently, Vietnam has the Verorab vaccine (France) and the Abhayrab vaccine (India) to prevent rabies. The regimen for people who have never been vaccinated includes 5 injections on days 0-3-7-14-28 (for intramuscular injection) or 4 injections on days 0-3-7-28 (for intradermal injection). In case of level III exposure, it is necessary to combine injection of anti-rabies serum. In case of proactive vaccination before being bitten by a dog or cat, the regimen will include 3 injections on days 0-7-21 or 0-7-28.
Nhat Linh
More than 120 centers of the VNVC Vaccination System have full vaccines to prevent infectious diseases for children and adults. All vaccines are stored safely, of high quality and have a system to look up vaccination schedules, remind vaccination schedules via text messages, and support correct and complete vaccination regimens.
Source link

































![[Photo] The 9th Congress of the Party Committee of the Office of the President, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/20/78e7f27e8c4b4edc8859f09572409ad3)






















![[Maritime News] Wan Hai Lines invests $150 million to buy 48,000 containers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/20/c945a62aff624b4bb5c25e67e9bcc1cb)











































Comment (0)