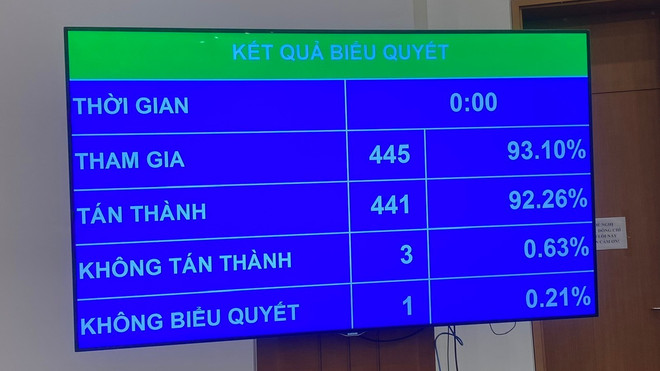
On the morning of June 14, with 441/445 delegates participating in the vote in favor, the 9th Session of the 15th National Assembly officially passed the Law on Digital Technology Industry.
This Law regulates the development of digital technology industry, semiconductor industry, artificial intelligence, digital assets, rights and responsibilities of relevant agencies, organizations and individuals.
Before voting, Chairman of the National Assembly's Committee on Science , Technology and Environment Le Quang Huy presented a report explaining, accepting and revising the draft Law on Digital Technology Industry.
Mr. Huy said that regarding digital assets, there are opinions that it is necessary to build a legal framework for digital assets that specifies core issues, immediately identifies the contents that must be implemented (property rights, ownership, transactions, security, responsibility, dispute resolution, risk management) ..., while ensuring consistency with the current legal system and international practices, while establishing a mechanism for management, supervision, and risk prevention; clarifying whether digital assets can be used for exchange or investment purposes; proposing to clarify the content and criteria for classifying digital assets.
In addition, according to the draft Law, digital assets have been defined as assets under current civil law. Property rights, ownership, transactions, security, liability, dispute resolution, risk management, etc. have been regulated under the provisions of criminal law, anti-corruption and anti-money laundering laws and related laws.
Therefore, in order to ensure the feasibility, flexibility and stability of the legal system, the draft Law only stipulates principles on this issue and assigns the Government to make specific regulations in accordance with development practices.
Incorporating the opinions of National Assembly deputies, the draft Law has more specifically stipulated a number of core contents in State management of digital assets (including the creation, issuance, storage, transfer, and establishment of ownership of digital assets; rights and obligations of parties regarding activities related to digital assets; measures to ensure information security and network security; prevention and combat of money laundering, prevention and combat of terrorist financing, and financing of proliferation of weapons of mass destruction; inspection, examination, and handling of violations of the law; business conditions for providing cryptographic asset services...), and at the same time, assigned the Government to specify in detail the authority, management content, and classification of digital assets in accordance with the practice and management requirements in sectors and fields.
The Law also stipulates a number of policies for developing the digital technology industry, including mobilizing investment resources for research, development, design, and technology transfer; gradually mastering digital technology; building shared digital technology industry infrastructure on a regional and national scale to promote digital technology industry activities.
In addition, train and develop human resources for the digital technology industry; develop educational institutions and vocational training institutions specializing in digital technology; have special incentive mechanisms to attract and employ high-quality digital technology human resources and digital technology talents.
The Law on Digital Technology Industry also establishes a controlled testing mechanism for products and services applying digital technology in industries and fields, including a mechanism to exclude liability for agencies, organizations, businesses and individuals in testing.
Along with that, there are preferential mechanisms on land, credit, tax and other preferential mechanisms in research, testing, development, production, application of digital technology products and services. Next is to develop the market for the digital technology industry; there are mechanisms for ordering, prioritizing investment, renting, purchasing digital technology products and services using state budget capital.
In addition, developing digital data in digital technology industry activities becomes an important resource, means of production and a foundation for research, development, and promotion of the digital technology industry, while promoting the development and application of artificial intelligence in industries, fields and aspects of socio-economic life; making artificial intelligence a new production method; strongly promoting national endogenous capacity, creating new economic models with outstanding productivity and value. The State has the highest preferential policies to promote, research, develop, deploy and use artificial intelligence.
The Law on Digital Technology Industry also has outstanding preferential policies to develop the semiconductor industry, forming a Vietnamese semiconductor ecosystem. As well as developing a sustainable digital technology industry, using energy economically and efficiently, minimizing negative impacts on the environment./.
On transitional provisions
During the period when laws, resolutions of the National Assembly, ordinances and resolutions of the National Assembly Standing Committee have not been amended or supplemented within 02 years from the effective date of this Law, the Government shall issue legal documents to resolve difficulties and obstacles for the development of the digital technology industry as prescribed in the articles, clauses and points of laws, resolutions of the National Assembly, ordinances and resolutions of the National Assembly Standing Committee for unified application, and periodically report to the National Assembly Standing Committee; in cases related to laws and resolutions of the National Assembly, report to the National Assembly at the nearest session.
Source: https://www.vietnamplus.vn/quy-dinh-cu-the-mot-so-noi-dung-cot-loi-trong-quan-ly-nha-nuoc-ve-tai-san-so-post1044205.vnp



































































































Comment (0)