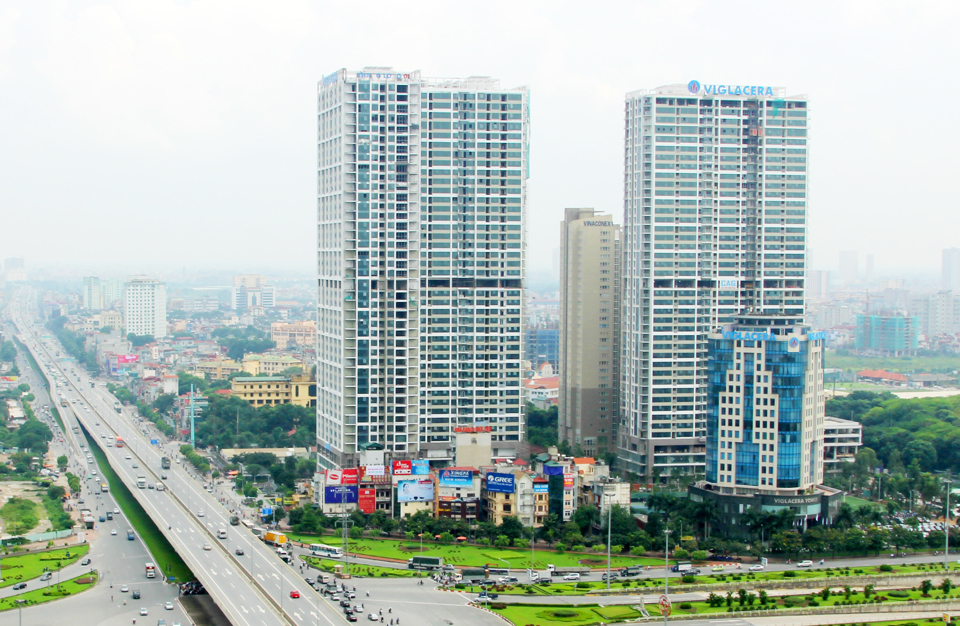

Indispensable element
According to statistics, the Ministry of Construction said that currently, the country has over 400 green buildings with a total floor area of about 10 million m2. The number of buildings certified as green buildings, using energy economically and efficiently has exceeded the target set in Decision No. 280/QD-TTg of the Prime Minister approving the National Program on energy saving and efficiency for the period 2019 - 2030.
According to Decision 280, the goal is that by 2025, the whole country will have 80 construction works certified as green buildings, using energy economically and efficiently; by 2030, it will reach 150 works. Currently, the number of green buildings in Vietnam is at a fairly average level in the ASEAN region.
Green buildings have been developed in the world since the 1990s and have gradually become a movement and trend in investment, construction and operation management of buildings in over 100 countries and territories. In Vietnam, green buildings first appeared around 2005 - 2010. In 2023, Vietnam ranked 28th in the world in terms of the number of green buildings assessed according to the LEED Standard for green building assessment and certification of the US Green Building Council.
Industry experts believe that green technology and materials play an important role in evaluating sustainable green buildings. In particular, green facade design is an important factor that needs to be considered to minimize the impact of construction on the environment and human life.
In addition, the application of green technology to the facade of architectural works is not only related to the quality of architectural aesthetics but also promotes many aspects of energy saving. With optimal facade design, it will help save energy in the operation of the building.
Multiple construction solutions
At the recent workshop “Sustainable facade solutions for green buildings”, Worklounge 03 Sustainable Environmental Design Director, Architect Tim Middleton, presented two passive design solutions to reduce heat absorption by using reflective insulation panels on the roof, or creating green roofs and walls, reducing heat transfer efficiency by using insulation chambers.
In particular, the design of the building's shell is based on the principle of placing the building in the North-South direction if possible, reducing the ratio of windows in the East-West direction, avoiding direct sunlight through the skylight (using high windows instead), using a roof with high reflectivity, increasing roof insulation, shading and sun protection, using Low-E/Solar Control glass or double-glazed glass.
This design can save 20% of the building energy. Passive design before conception will be more efficient in construction and use, can reduce energy in the building up to 60%, investment costs will be lower and achieve higher efficiency.
According to Amos Seah, Senior Manager of EDGE BOND Solutions at Technoform Singapore, preliminary statistics in Vietnam show that glass accounts for 90% of commercial buildings, while the figure is 70% in residential buildings. Aluminum frames also absorb a lot of heat, but there are no specific regulations. Many countries like Singapore have strict regulations on double-glazed glass, with a heat absorption rate of only 2-3%.
According to Mr. Seah, the solution to optimize the building's energy efficiency is to apply a high-performance facade system with a solution to conduct heat through opaque walls, conduct heat through glass doors, reduce solar radiation through glass doors, reduce heat in glass frames and glass edges. The materials used are DGU laminated glass coated with Low-E, IGU spacers have improved the heat absorption efficiency of the glass surface as well as the window frame.
Source: https://kinhtedothi.vn/mat-dung-ben-vung-cho-cong-trinh-xanh.html























![[Photo] Nghe An: Provincial Road 543D seriously eroded due to floods](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/5/5759d3837c26428799f6d929fa274493)










































































Comment (0)