According to Khmertimeskh, in early June, in Beihai City (Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China), Cambodia and China signed major trade cooperation agreements on agricultural products, notably two memorandums of understanding on exporting 20,000 tons of dried mango and 15,000 tons of fresh durian from Cambodia to China, in the period of 2025-2027.
Cambodian fruits enter Chinese market
As for dried mangoes, China has committed to importing about 3,000 tons this year. This is part of a long-term strategy to expand the agricultural trade corridor between the two countries.

This move comes less than two months after Cambodia and China signed a phytosanitary protocol for fresh durian (April 17), officially paving the way for this popular tropical fruit to enter the "race" in the Chinese market - which consumes more than 85% of the total global durian output.
At the end of April, the first shipment of fresh durian from Cambodia was also exported to China.
Not only stopping at documents, China is actively investing in the Cambodian fruit industry. In Battambang province, China's Zhengzhou Chen Group has cooperated with local enterprises to develop a 165-hectare durian plantation, which is in the infrastructure construction phase.
With Cambodia’s rapid entry into the Chinese fruit market, the list of fruits allowed for direct export from the country to China has been expanded to five: bananas, mangoes, longans, coconuts and durians. Negotiations on pineapples and jackfruit are also underway.
Vietnam's fruit market share under pressure
Cambodia's increased presence in the Chinese market has put Vietnam - the leading agricultural exporter to China - in direct competition, especially in two key product groups: mango and durian.
Vietnam's fresh mango exports in the first quarter reached 88.5 million USD , besides, processed mango products also brought in 29.3 million USD .
Of which, Vietnam accounts for 97% of China's total mango import turnover, equivalent to nearly 29 million USD , far surpassing competitors such as Thailand, Peru, Australia, Philippines and even Cambodia. The current price of Vietnamese mangoes fluctuates around 700 USD /ton - equal to Cambodia and much lower than other countries (6,000- 11,000 USD /ton).
For durian, Vietnam is currently the second largest supplier to China after Thailand. In the first four months of the year, Vietnam exported about 35,000 tons of durian to China.
In April alone, China spent up to 345 million USD to import more than 61,000 tons of durian from many countries - up 270% compared to the previous month, according to Produce Report.
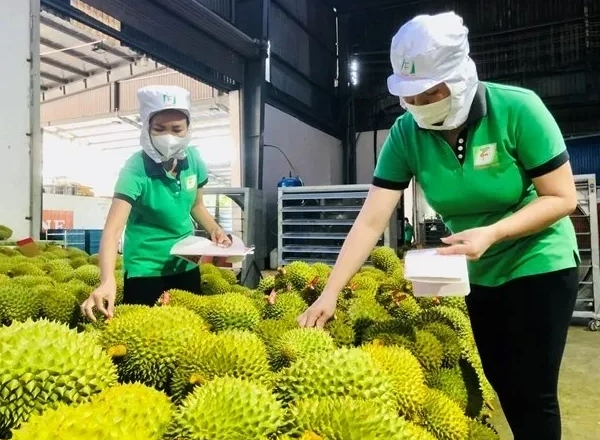

China is considered a large and potential market for fruit exports. In the context of Cambodia gradually entering this playing field, it has created more competitive pressure in terms of output, quality and market share with Vietnam.
Mr. Dang Phuc Nguyen - General Secretary of the Vietnam Fruit and Vegetable Association - said: The key factors that help Vietnamese fruits gain an advantage in the Chinese market are competitive prices, low logistics costs, geographical proximity and long growing seasons.
However, China's continuous opening of its market to Cambodian fruits, accompanied by direct investment from importing enterprises, shows that the country is promoting the diversification of supply sources and gradually reducing its dependence on a few large markets such as Vietnam or Thailand.
Vietnam needs to accelerate investment in the value chain, improve growing standards, and diversify its markets if it does not want to be pushed out of its main market. In the context of Cambodia constantly expanding its permitted export products and receiving many preferential policies from China, Vietnam needs a more systematic strategy to maintain its market share.
Source: https://baoquangninh.vn/how-do-vietnamese-fruits-change-when-china-quoc-increases-import-of-other-countries-3363064.html


































































































Comment (0)