In the context of globalization and strong development of e-commerce, counterfeit goods are becoming a transnational problem, causing serious damage to the interests of consumers, businesses and the reputation of the economy . Faced with this challenge, many countries have built systematic, synchronous and effective anti-counterfeiting strategies.
The recent discovery of a series of counterfeit goods production and trading cases in Vietnam has shown the increasing scale and sophistication of this type of economic crime.
China
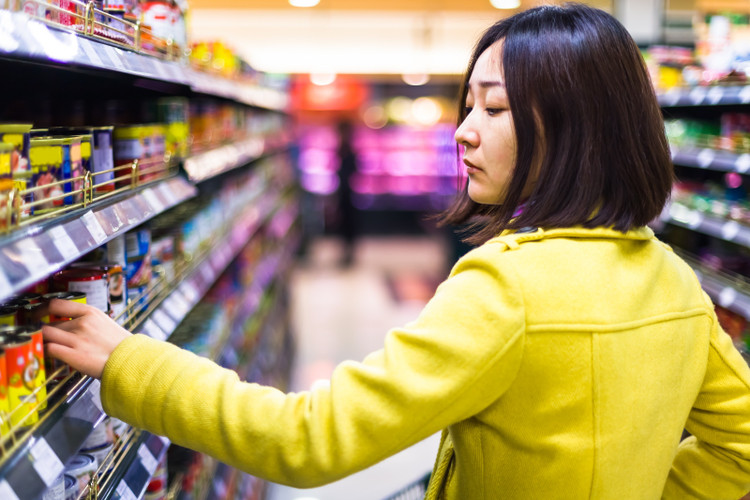
China was once considered one of the world’s largest counterfeit “factories,” with counterfeit goods ranging from fashion and electronic components to medicines and food being produced and smuggled onto the market on a massive scale. However, over the past decade, the Chinese government has implemented a series of tough measures to curb and push back the problem, from improving the legal system, strengthening enforcement, to applying technology and cooperating with the private sector.
One of the most important measures is China's continuous improvement of its legal framework for protecting intellectual property rights. The Trademark Law has been amended to increase penalties and allow authorities to take stronger enforcement measures. Serious infringements can be prosecuted criminally, instead of just administratively. Specialized intellectual property courts have also been established in major cities such as Beijing, Guangzhou and Shanghai, helping to speed up the trial process and improve the expertise in dispute resolution.
The Chinese government has rolled out a series of tough measures to curb and push back the counterfeiting problem. Photo: Campaign Asia.
In parallel, China has established specialized anti-counterfeiting forces within the police, customs and market management systems. These forces regularly coordinate with each other to detect and destroy large-scale counterfeit production and distribution chains. A series of nationwide crackdown campaigns have been launched, especially during peak times such as before Tet.
One particularly notable aspect of China’s anti-counterfeiting experience is the use of technology corporations, especially in the e-commerce environment. Large platforms such as Alibaba, JD.com and Pinduoduo have established artificial intelligence and big data systems to detect infringing products early, while also working with authorities to remove stores, trace their origins and support legal proceedings. Many companies have also deployed traceability technology using QR codes or blockchain, helping consumers authenticate goods right from the purchase stage.
Although counterfeiting still exists, China’s strong efforts have contributed to significantly reducing the prevalence of counterfeit goods in the domestic market. This is a remarkable lesson for developing countries in closely combining legal policies, strict enforcement and the application of modern technology in the work of preventing and combating counterfeiting.
Japan
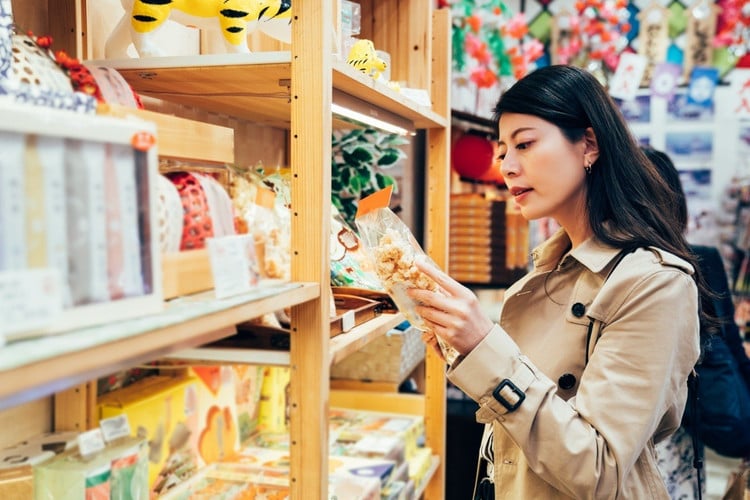
Japan has one of the lowest counterfeiting rates in the world, thanks to its strict legal system, high social awareness and effective coordination between government agencies, businesses and consumers. Japan’s experience in combating counterfeiting is not only based on legal sanctions but also built on a foundation of culture, education and technology.
First of all, Japan has a very strict legal system for protecting intellectual property rights, including the Trademark Law, Patent Law, Design Law and other copyright-related documents. Intellectual property infringements such as the production, possession or sale of counterfeit goods are strictly handled, which can lead to criminal penalties and large civil compensation. In addition, the Japanese government has established specialized units within the police and customs forces to monitor and handle cases related to counterfeit goods, especially at border gates and large commercial centers.
Japan has one of the lowest counterfeiting rates in the world. Photo: Campaign Asia.
One of the important factors contributing to Japan's success is the combination of law enforcement and raising public awareness. Right from the primary school level, Japanese education has integrated intellectual property rights, consumer ethics and respect for genuine products into the curriculum. Thanks to that, Japanese people are very aware of choosing goods with clear origins, and are ready to denounce acts of counterfeiting to the authorities. Consumer protection associations in Japan are also very active in monitoring the market, providing legal advice and detecting suspicious goods.
In addition, Japan is constantly applying technology to prevent counterfeit goods. Large enterprises in Japan often use product authentication measures using QR codes, multi-layer anti-counterfeit stamps, or smart traceability technology. These solutions not only help consumers easily check goods but also support authorities in monitoring and investigating.
Japan's experience in fighting counterfeiting shows that a transparent, disciplined society with an effective legal system will create an environment where counterfeiting is virtually impossible.
Singapore
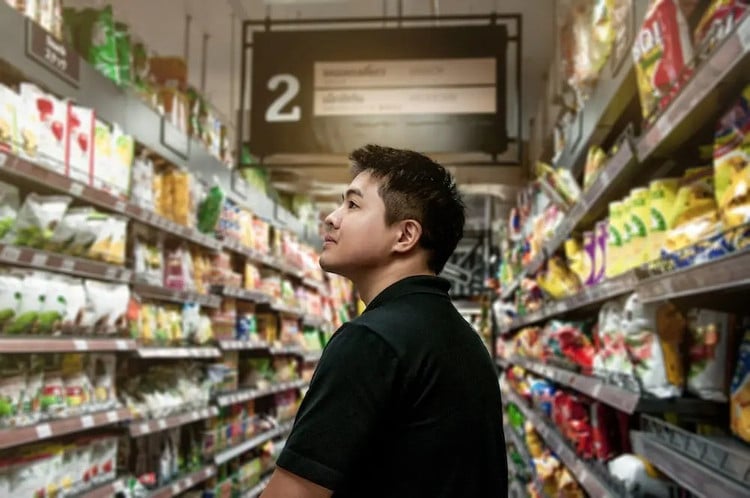
Singapore is one of the leading countries in Asia in creating a transparent, clean and virtually counterfeit-free trading environment. As a regional financial, trade and logistics hub, Singapore places great emphasis on protecting intellectual property rights and maintaining trust in the distribution system. The island nation’s experience in combating counterfeiting is a combination of strict laws, effective enforcement mechanisms, advanced technology and a strong sense of social integrity.
First of all, Singapore has a very strong legal system on intellectual property rights, including laws on trademarks, copyrights, patents and industrial designs. The production, distribution and possession of counterfeit goods are all considered serious violations and can be criminally prosecuted with high penalties, including imprisonment. Beyond just legal regulations, the Singapore government also invests heavily in enforcement.
The production and consumption of counterfeit goods is virtually non-existent in Singapore. Photo: Pelago.
The Intellectual Property Office of Singapore (IPOS) plays a central role in receiving and handling complaints and coordinating with agencies such as the police, customs and market regulators to investigate and crack down on counterfeiting cases. The Singapore customs system is equipped with modern inspection technology and has the right to temporarily detain suspected infringing goods at the border for timely inspection and handling.
One highlight of Singapore’s model is the role of businesses in combating counterfeiting. Large companies, especially in the pharmaceutical, electronics and high-end consumer goods sectors, regularly work with the government to implement market surveillance programs, trace product origins and train employees to identify counterfeit goods. Many brands use QR coding technology, anti-counterfeiting stamps integrated with digital technology or even blockchain to ensure the authenticity of goods in circulation.
In addition, Singapore is also actively participating in international intellectual property agreements such as the Paris Convention, the Berne Convention, and the TRIPS Agreement under the WTO, thereby expanding its ability to cooperate and share information with other countries in tracing and preventing cross-border counterfeit goods.
Through a combination of legislation, enforcement, technology and public-private partnerships, Singapore has created a clean trading environment where the production and consumption of counterfeit goods are virtually non-existent. The Singapore model offers valuable lessons for developing countries in building a comprehensive and effective anti-counterfeiting system.
Source: https://khoahocdoisong.vn/cac-nuoc-chong-hang-gia-nghiem-ngat-the-nao-post1550531.html






![[Photo] Cuban artists bring "party" of classic excerpts from world ballet to Vietnam](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/26/797945d5d20b4693bc3f245e69b6142c)






![[INFOGRAPHIC] Who is the Supreme Leader of Iran?](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/26/37939efe33e041ada15c70727337321c)












![[e-Magazine] The miner with the heart of a hero and the mind of a scientist](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/26/939abd62908e447aa88b8c6a1d819764)



![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Australian Ambassador to Vietnam Gillian Bird](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/26/ce86495a92b4465181604bfb79f257de)








































































Comment (0)