People with gout can eat tilapia, red snapper, eel; avoid tuna, mackerel, sardines... because they contain a lot of purine, making the disease worse.
Gout is a common form of arthritis that occurs when excess uric acid builds up in the body, forming crystals in the joints. Symptoms include sudden, severe pain in the joints, accompanied by swelling and redness, which limits movement.
The most important nutritional principle for gout patients is to limit foods high in purine because this substance breaks down to create uric acid. Patients should eat enough and balanced fat, starch, protein, vitamins and minerals, but limit foods rich in purine such as red meat, seafood, animal organs... They have high protein content, leading to increased uric acid concentration in the blood, thereby causing gout.
Fish is rich in nutrients that are beneficial for heart health, but some are also high in purines and protein, so be careful.
Fish that contain no more than 100 mg of purine per 100 g serving include eel, monkfish, and sandfish. Catfish, flounder, snapper, ocean salmon, and tilapia are slightly higher in purine content but are also good choices. People with gout can fry, bake, boil, roast, or grill these fish.
Fish and seafood containing 100-200 mg of purine per 100 g such as carp, cod, flounder, haddock, black sea bass... should be consumed in moderation.
Patients should limit fish that contain 200 mg of purine or more per 100 g serving. Many types of fish and seafood have a high purine content, including crab, lobster, tuna, herring, perch, mackerel, sardines, scallops, and fjord trout. Eating a lot can cause an acute gout attack.
Purine content can vary between species and cooking methods. Boiling and steaming are healthy cooking methods because they do not require oil, butter or other fats, which helps reduce the overall purine content of the fish dish and preserves nutrients. Eating raw fish, such as sushi, has been linked to increased uric acid levels in the blood.
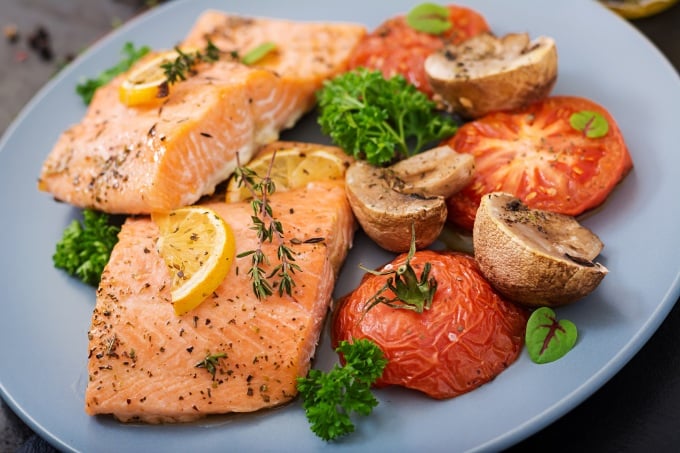

People with gout should eat fish in moderation, preferably steamed or boiled. Photo: Freepik
A study of more than 700 people by the American Rheumatology Foundation found that consuming omega-3 fatty acids helps reduce the number of gout flare-ups. Anchovies, herring, mackerel, haddock, salmon, sardines, bluefin tuna, striped bass... are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which help improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke. This is why the American Heart Association recommends eating two servings of fish per week. However, people with gout should eat fish in moderation.
There is currently no cure for gout. People can live with gout by maintaining a stable level of uric acid in the blood, thereby preventing the disease from developing.
Quit smoking, abstain from alcohol and stimulants, drink plenty of water to help eliminate excess uric acid from the kidneys, reduce symptoms of inflammation. Regular exercise helps reduce uric acid levels in the blood and restore joint flexibility after acute pain. Reducing stress and getting enough rest can prevent flare-ups.
In addition to diet, patients need to comply with the doctor's treatment, have regular check-ups or immediately when abnormalities are detected.
Mr. Ngoc (According to Verywell Health )
Source link



![[Photo] Cuban artists bring "party" of classic excerpts from world ballet to Vietnam](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/6/26/797945d5d20b4693bc3f245e69b6142c)
































































































Comment (0)