Many people in the communes of Bat Xat area and neighboring areas brought their children to Bat Xat Regional Medical Center to be screened by medical experts from E Hospital.
Doctors examined 250 children and discovered 2 cases of congenital heart disease and 15 cases of maxillofacial malformations.
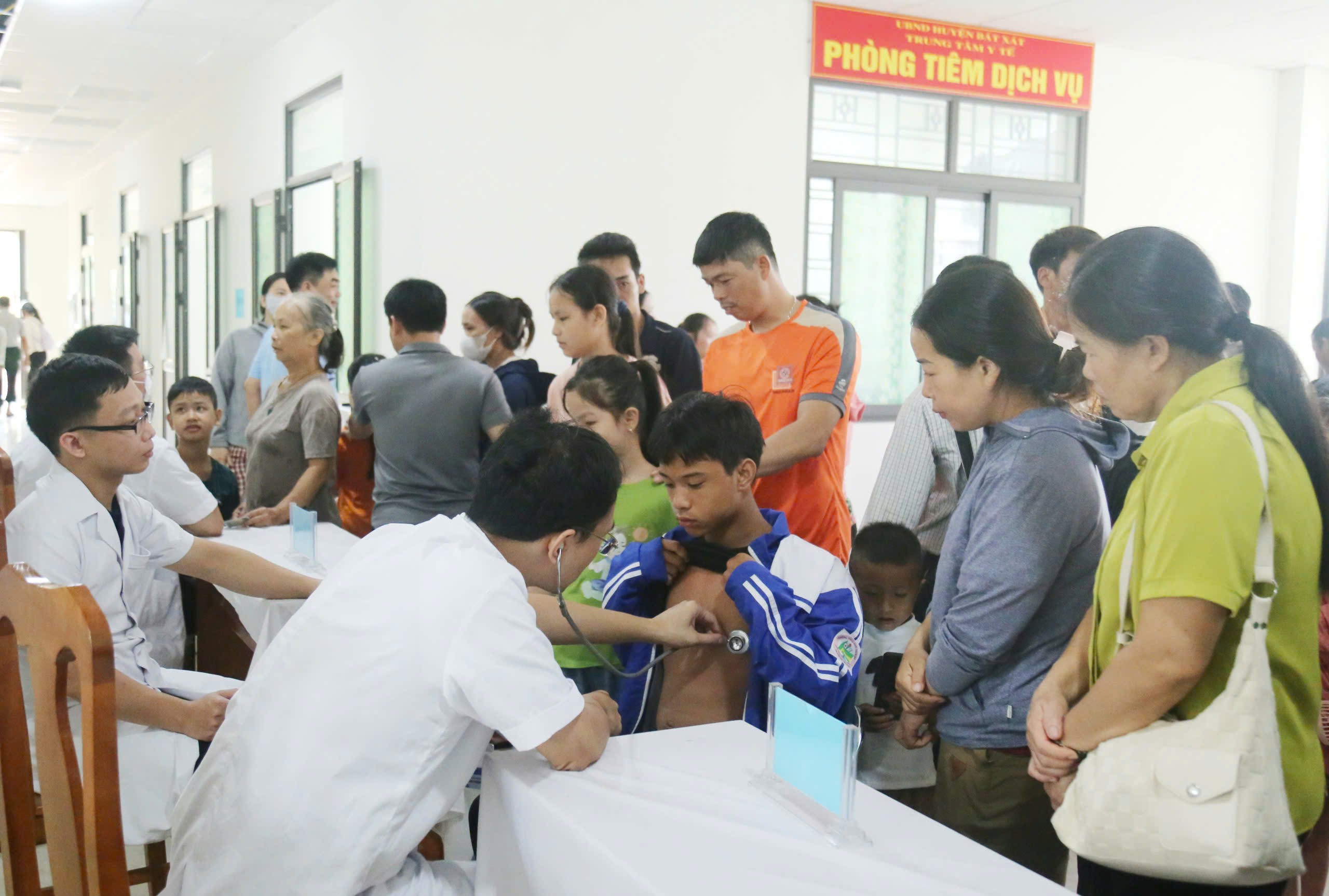
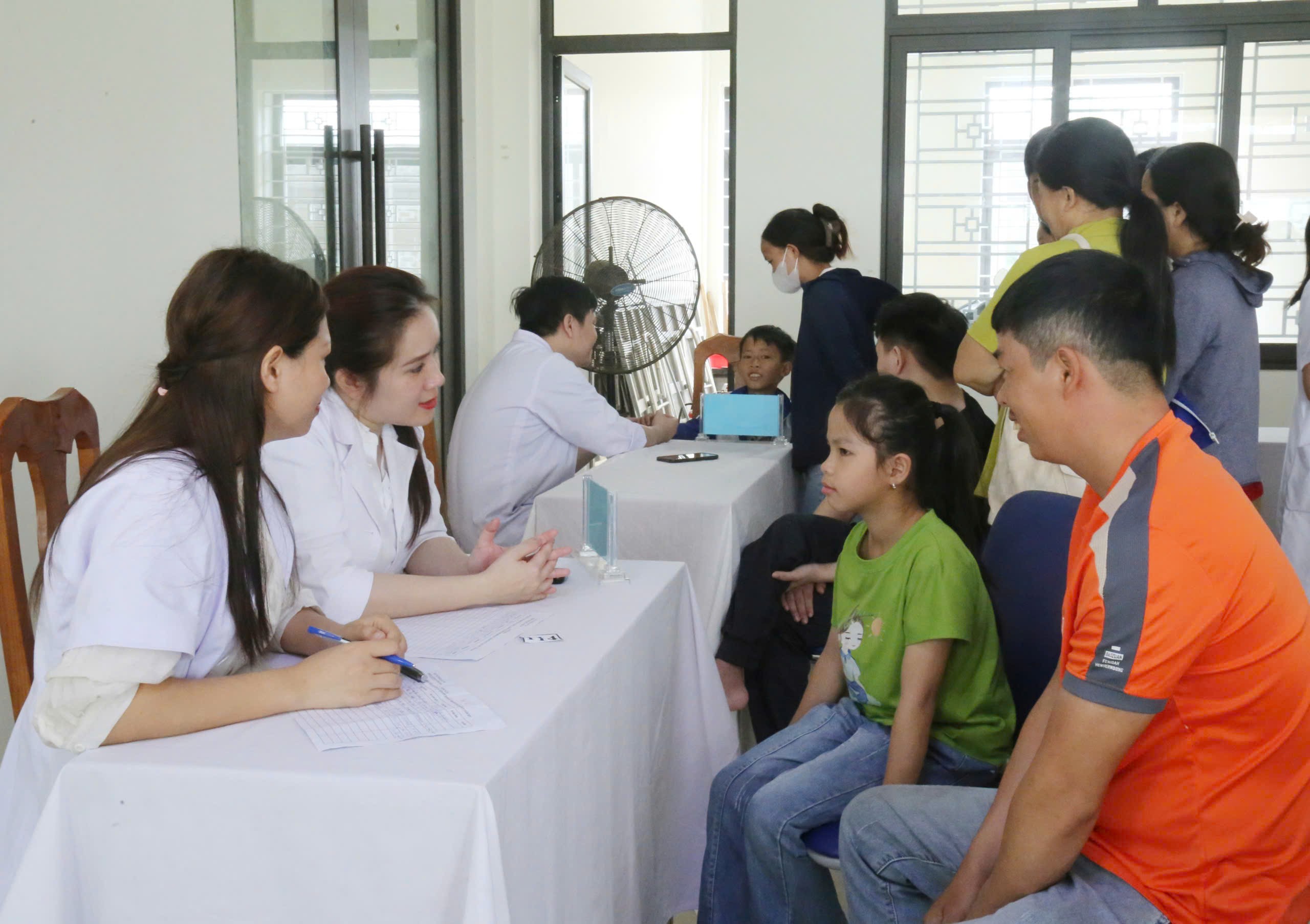


Previously, on September 12, the program was held in Bao Yen area, screening for disabilities for more than 200 children, thereby detecting 8 cases of congenital heart disease.
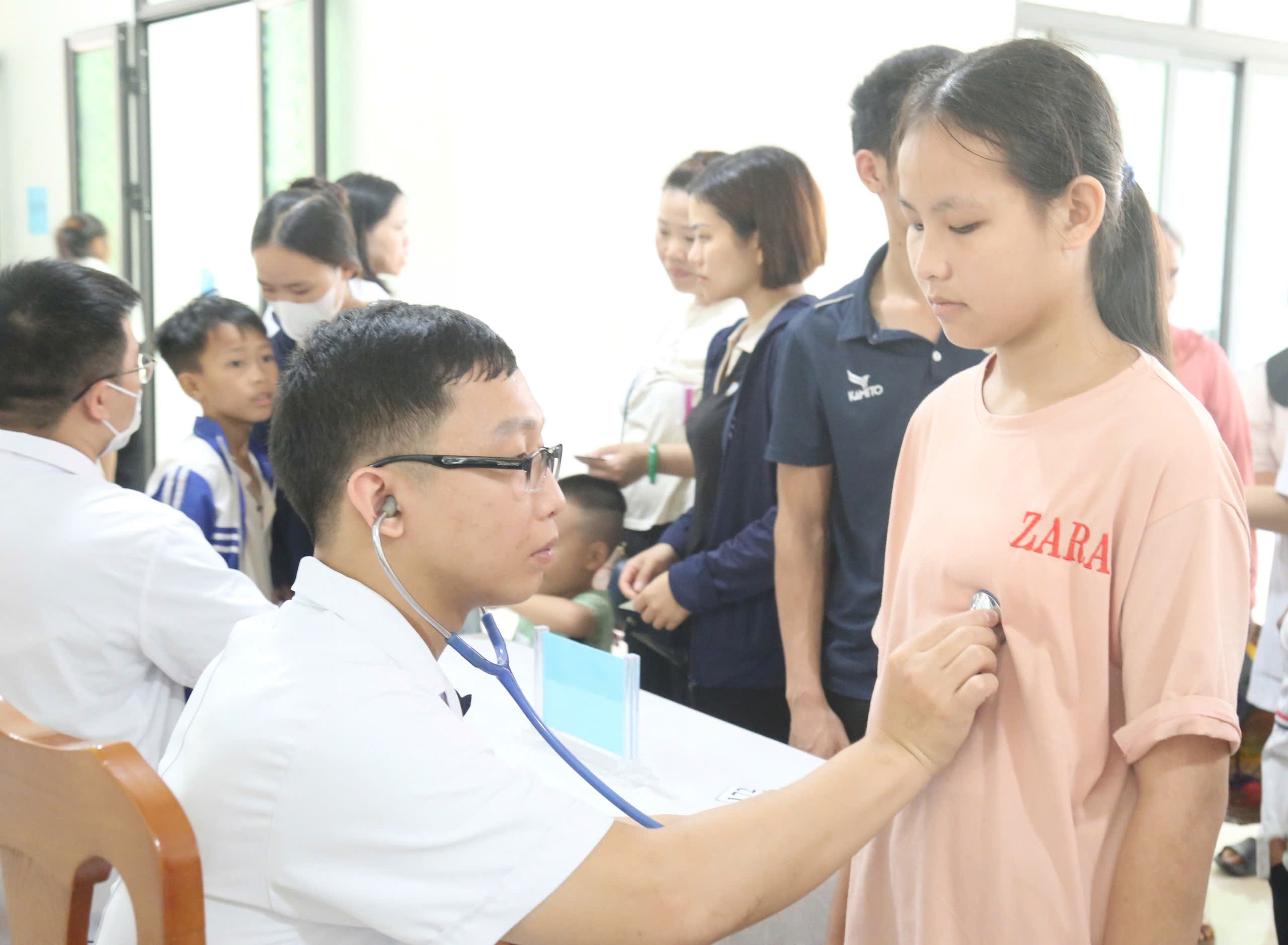
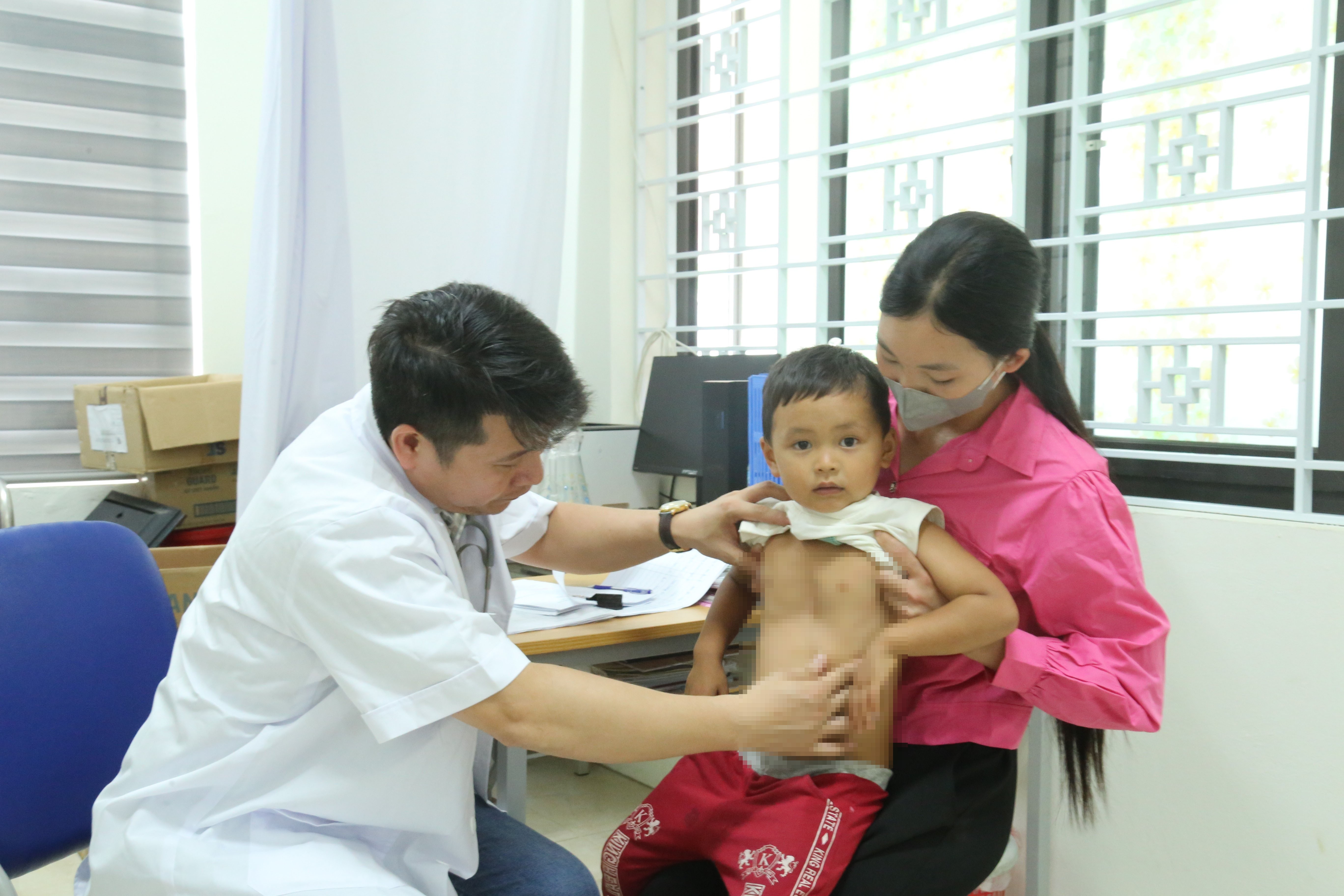

E Hospital's Cardiovascular Center has been accompanying the congenital heart screening program for children for 16 years in many provinces and cities across the country, aiming to detect diseases early in rural, remote and isolated areas - where conditions for cardiovascular examination, diagnosis and treatment are limited.
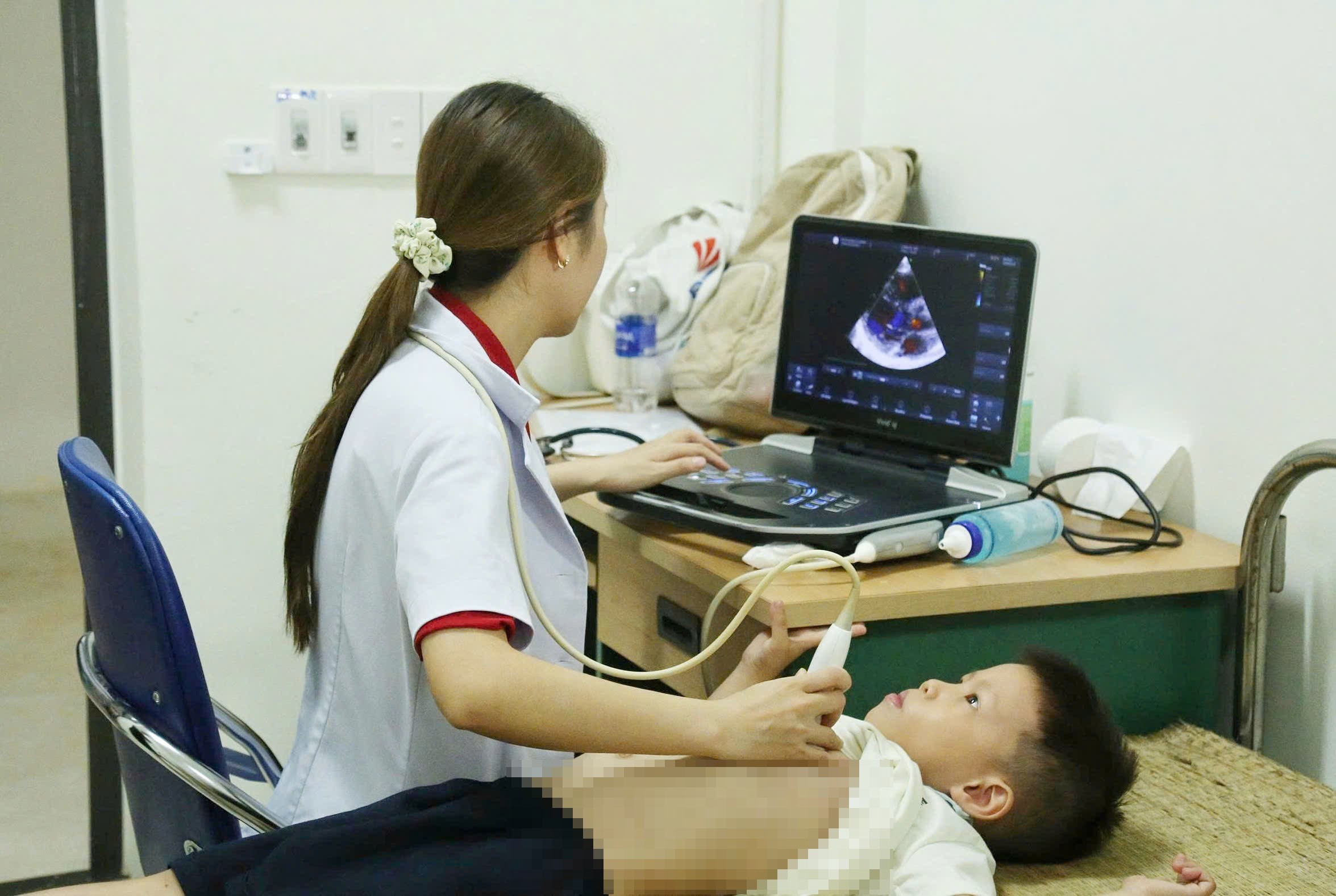

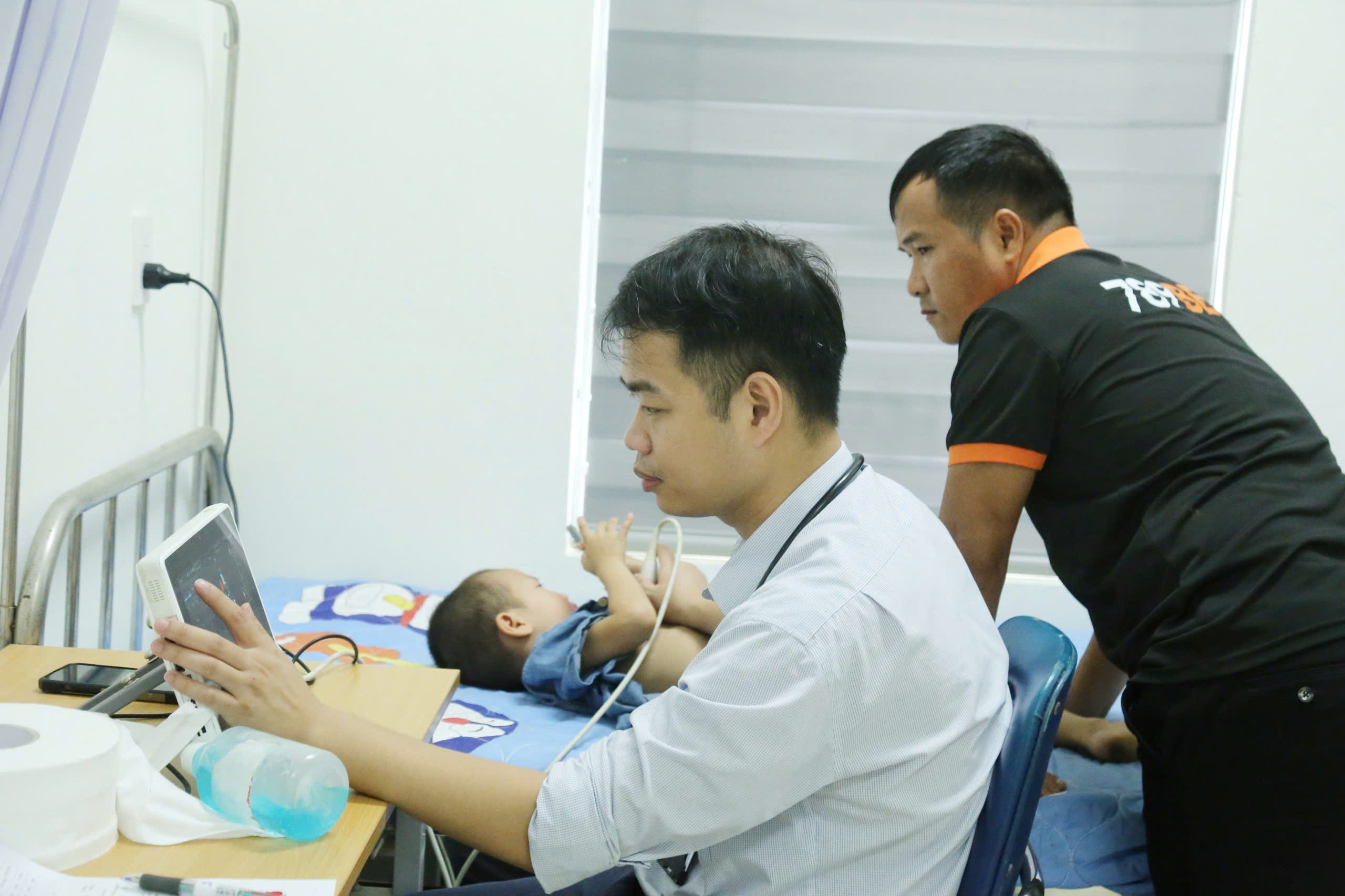
Children who are indicated for surgery by the hospital will be put on the priority list of the "Scars of Life" program of the Vietnam Children's Fund social enterprise to receive free heart surgery support.
Early detection and timely treatment will help increase the chances that children with congenital heart disease can grow up healthy, study and play like their peers.
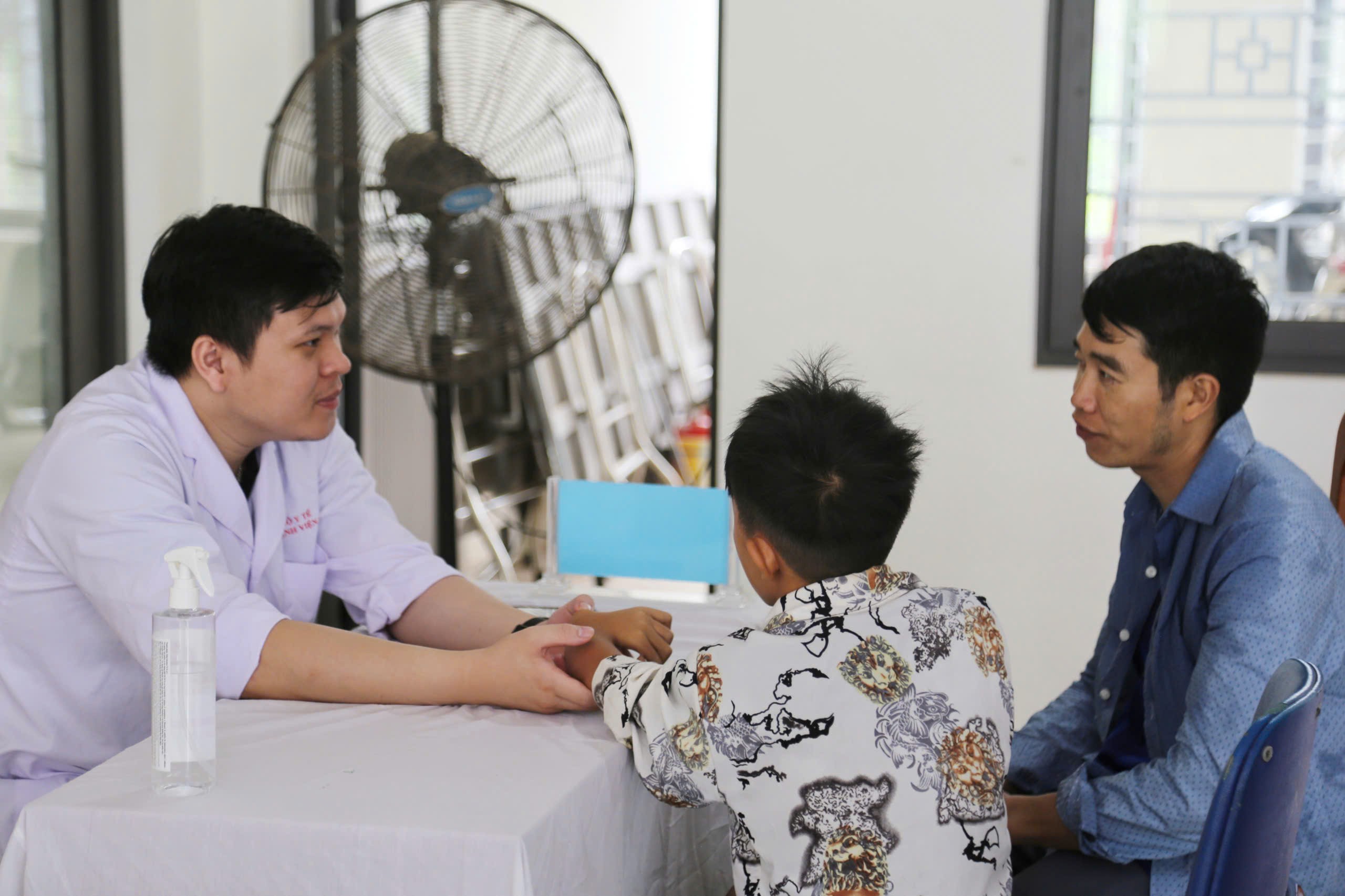

In May 2025, the program organized 2 examinations in Yen Bai province (old), screening 535 children, detecting 18 children with congenital heart disease, of which 13 children needed early intervention and surgery. Difficult cases were received by the "Scars of Life" program and supported with treatment costs.
On September 14, doctors at E Hospital will continue to screen children in the Sa Pa area.
The screening program is for children under 16 years old living in Lao Cai province, belonging to the following groups: children with congenital heart disease; cleft lip, cleft palate; eye disabilities (strabismus, ptosis, cataracts, glaucoma, corneal scars); children needing rehabilitation (motor impairment, speech delay, intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorder, brain sequelae, cerebral palsy, cerebrovascular accident, paralysis sequelae, motor delay due to premature birth, asphyxia, prolonged postpartum jaundice); children with motor disabilities (congenital defects of syndactyly, polydactyly, oligodactyly, bone defects; clubbed hands and feet; dislocated hips, patellas, shoulder joints, elbow joints; sclerosis of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, torticollis, fibrosis of the deltoid muscle, rectus femoris muscle, etc.).
Source: https://baolaocai.vn/250-tre-em-khu-vuc-bat-xat-duoc-kham-sang-loc-tim-bam-sinh-va-cac-di-tat-khac-post882019.html



![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 80th Anniversary of the General Department of Defense Industry](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/15/fb8fd98417bb4ec5962de4f7fbfe0f6a)

![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends the opening ceremony of the new school year at the National Defense Academy](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/15/c65f03c8c2984e60bd84e6e01affa8a0)






































































































Comment (0)